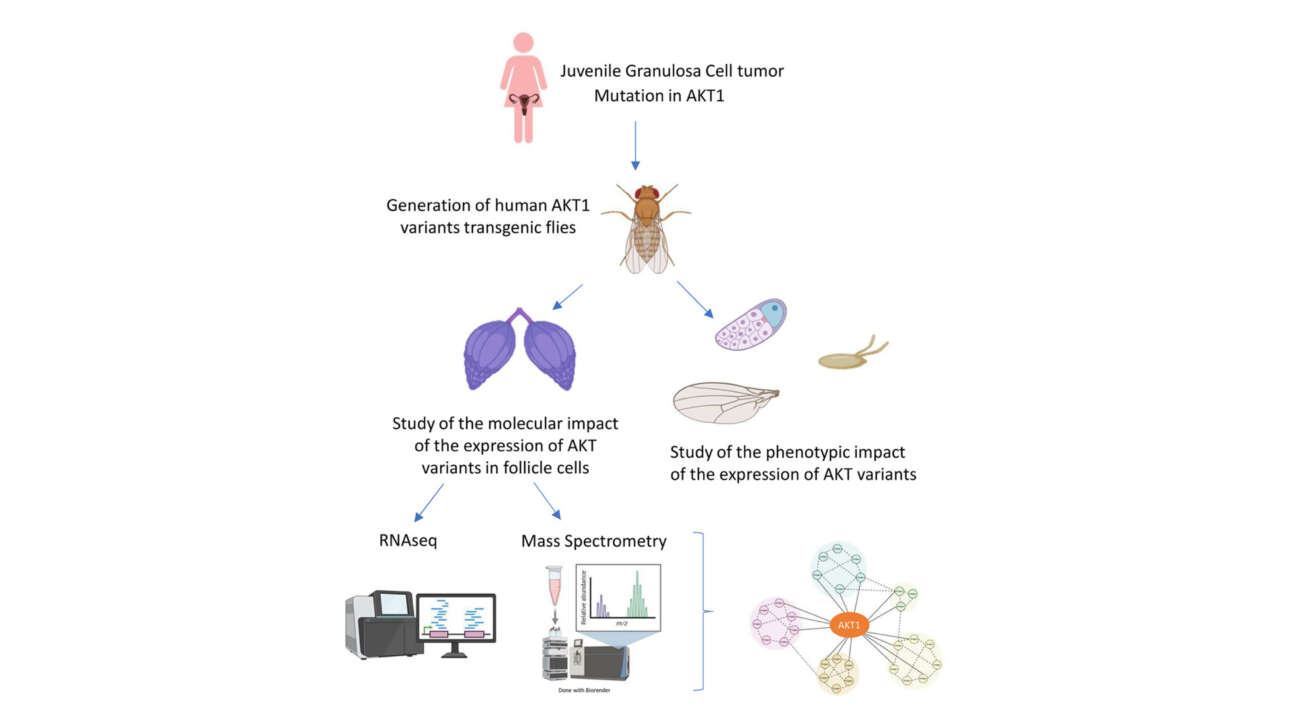
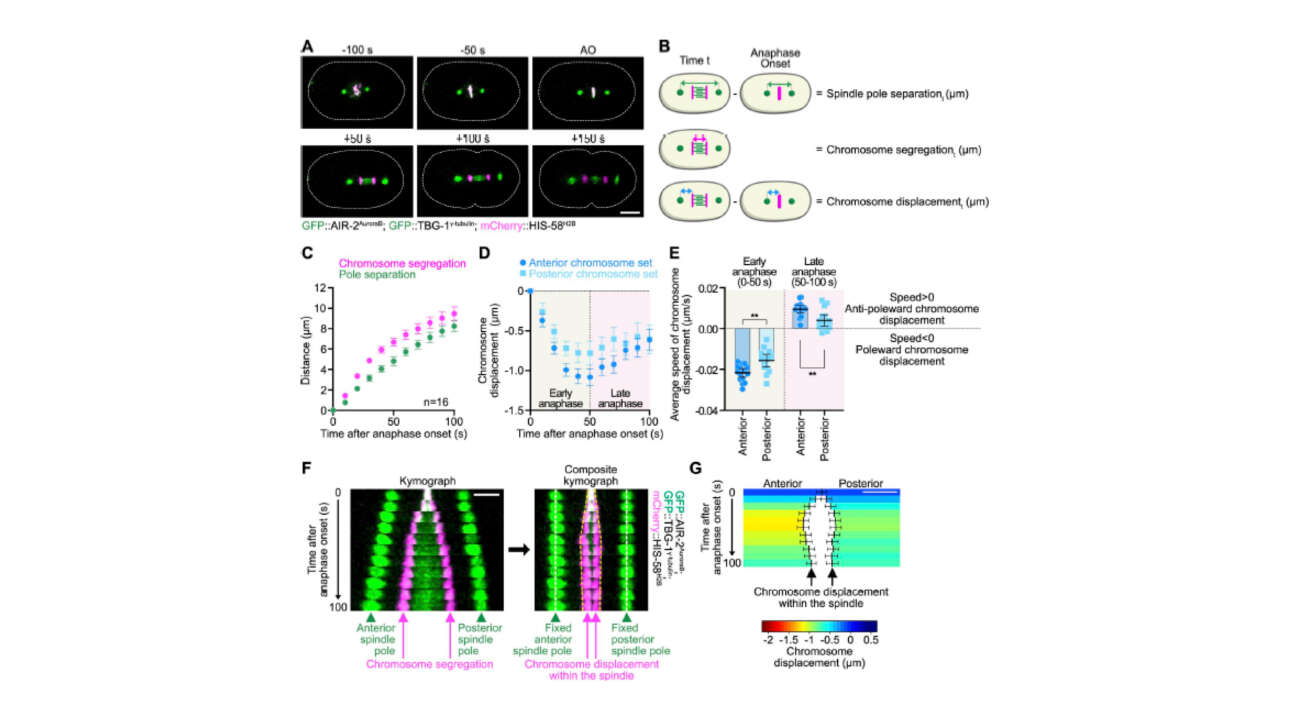
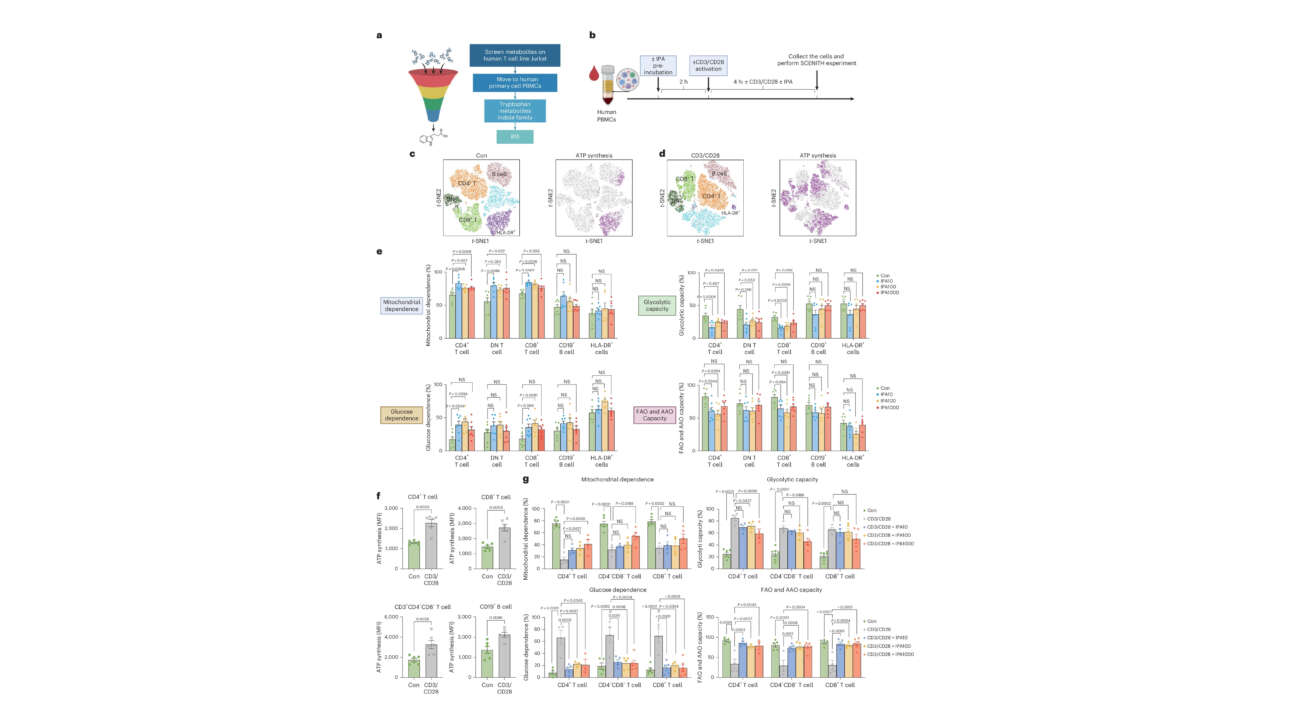
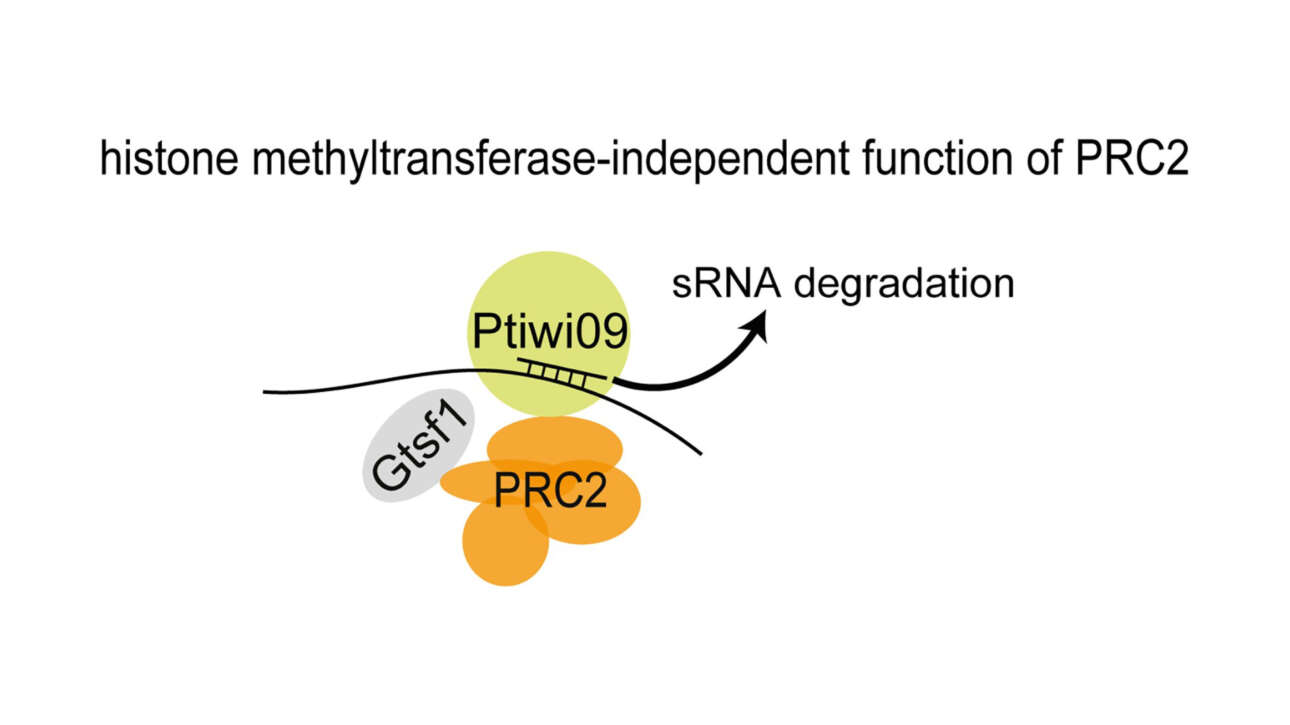
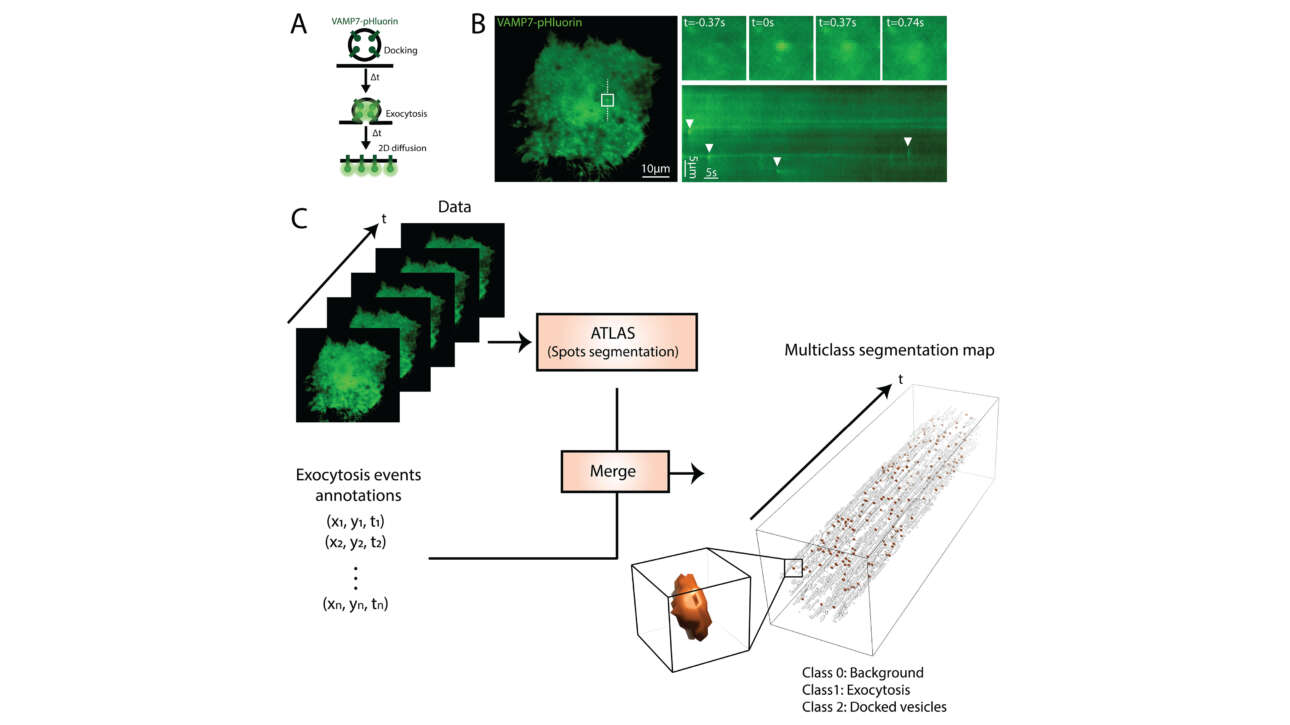
The Veitia Lab published a new article in Molecular & Cellular Proteomics: :
Deciphering the impact of AKT1 pathogenic variants in Juvenile Granulosa Cell Tumors Using a Drosophila model.
Abstract:
Background
Juvenile-type granulosa cell tumors (JGCTs) manifest during the prepubertal period as precocious pseudo-puberty and/or dysmenorrhea. We have previously identified pathogenic variants in AKT1 in JGCTs. This study aims…