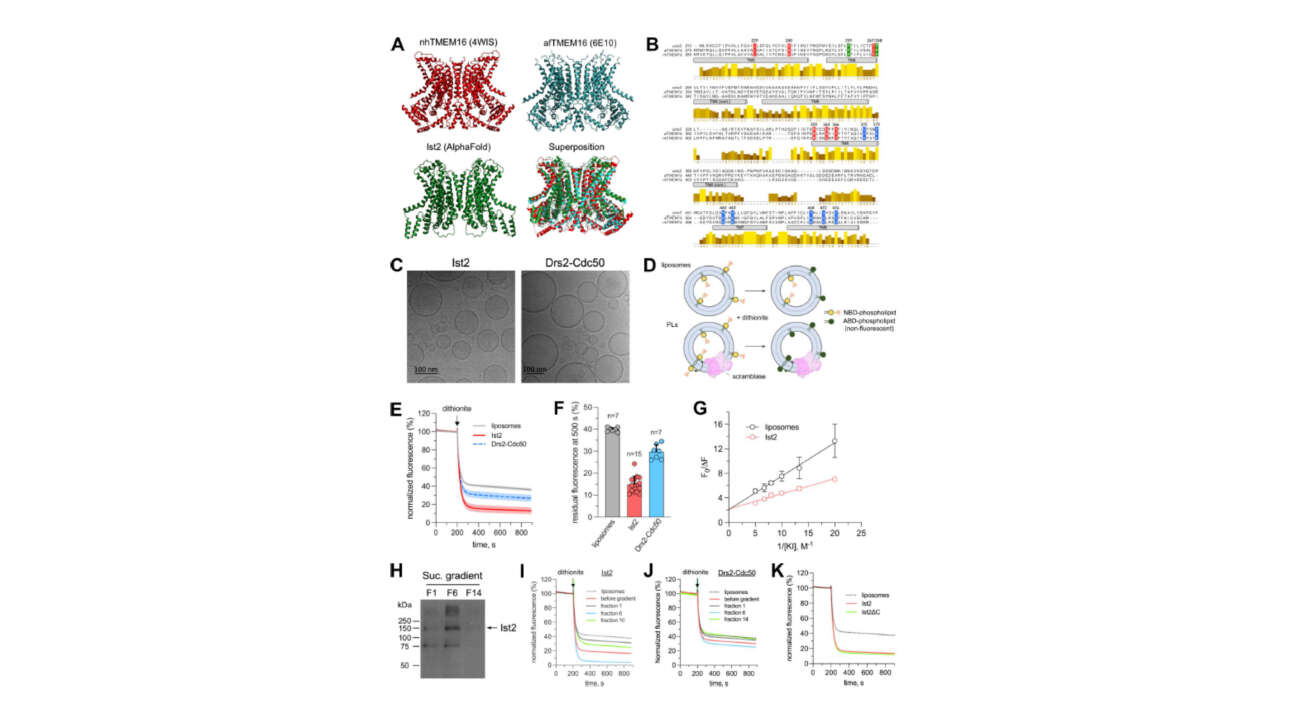
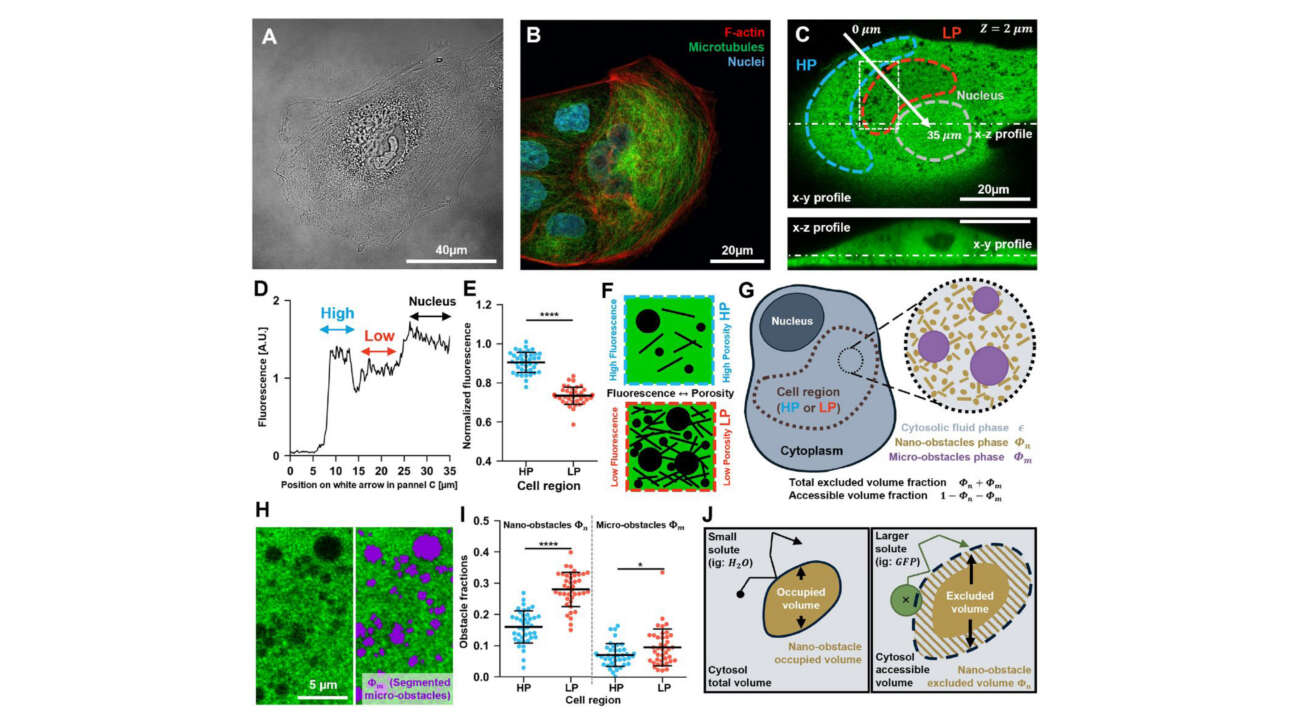
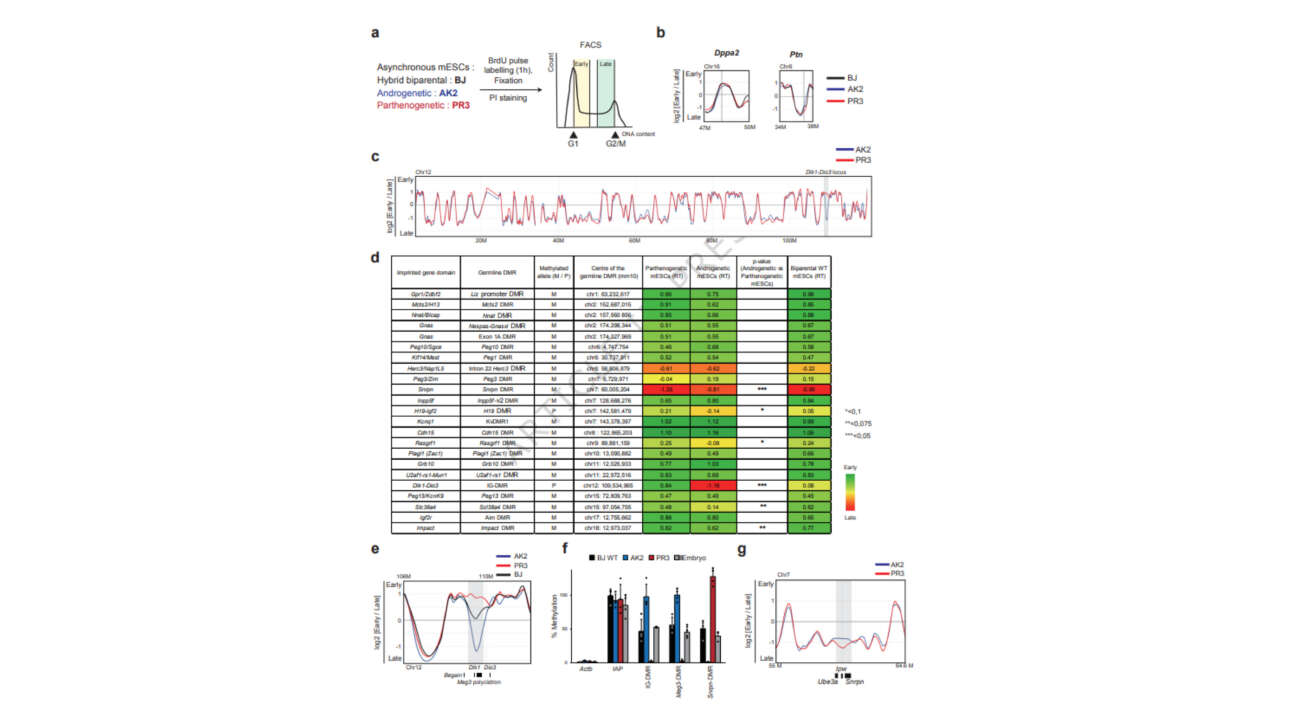
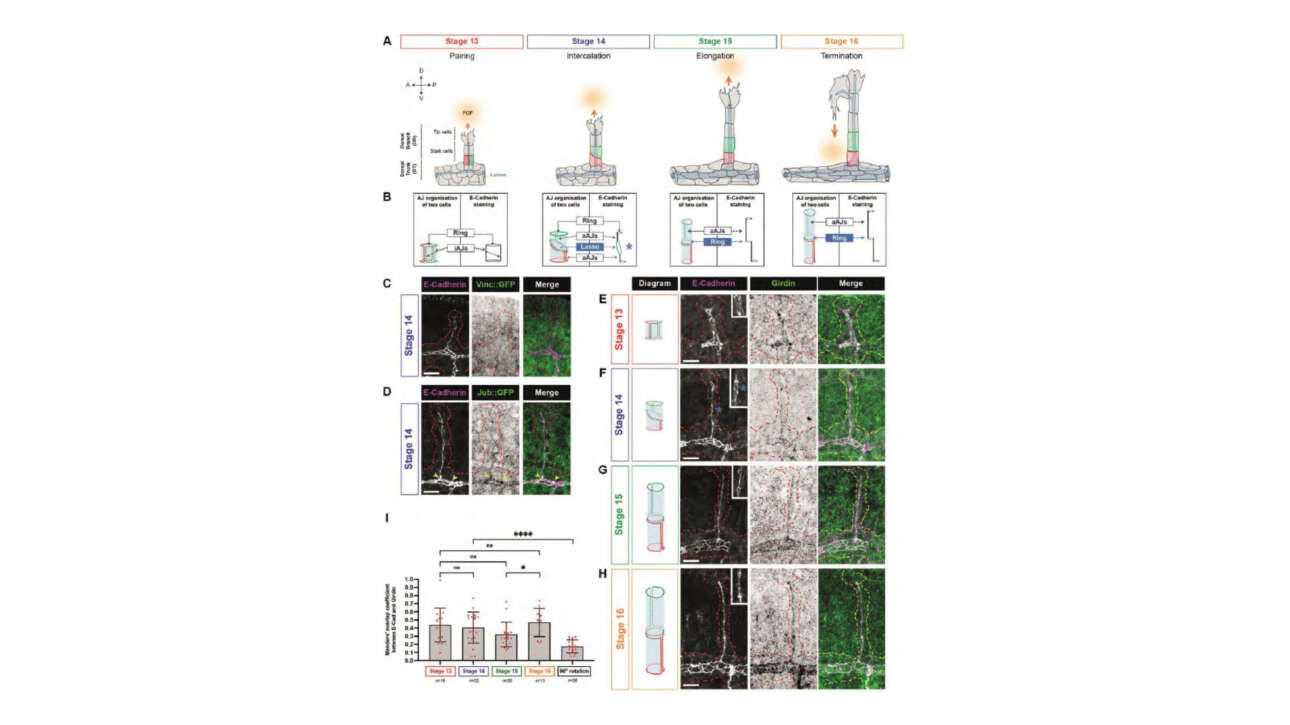
The Léon Lab contributed to the publication of a new article in Journal of Cell Biology:
Ist2 is a phospholipid scramblase that links lipid transport at the ER to organelle homeostasis
Abstract:
Lipid scramblases allow passive flip-flop of phospholipids between bilayer leaflets, thereby promoting membrane symmetry. At the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where phospholipid synthesis is restricted to…