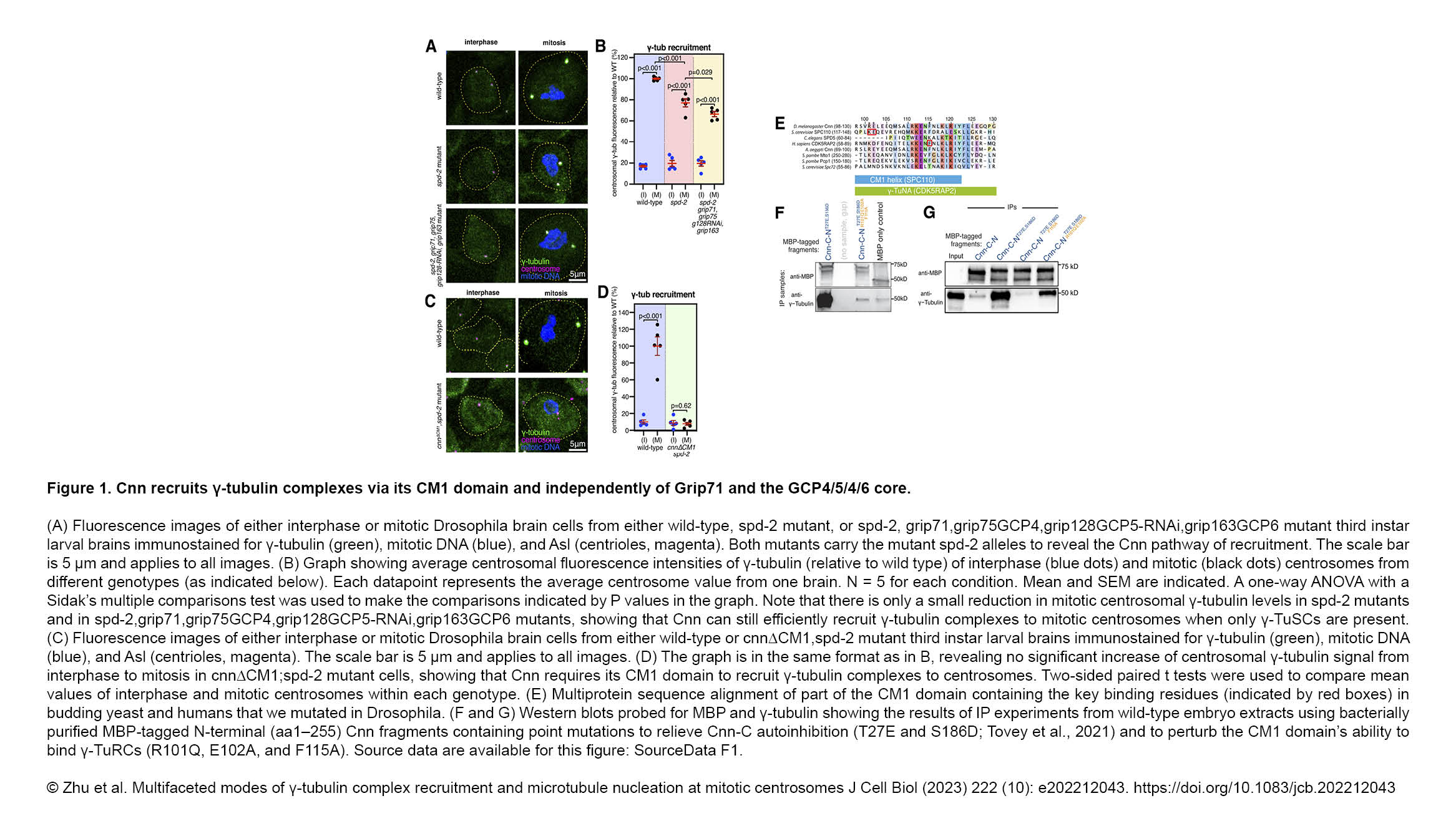
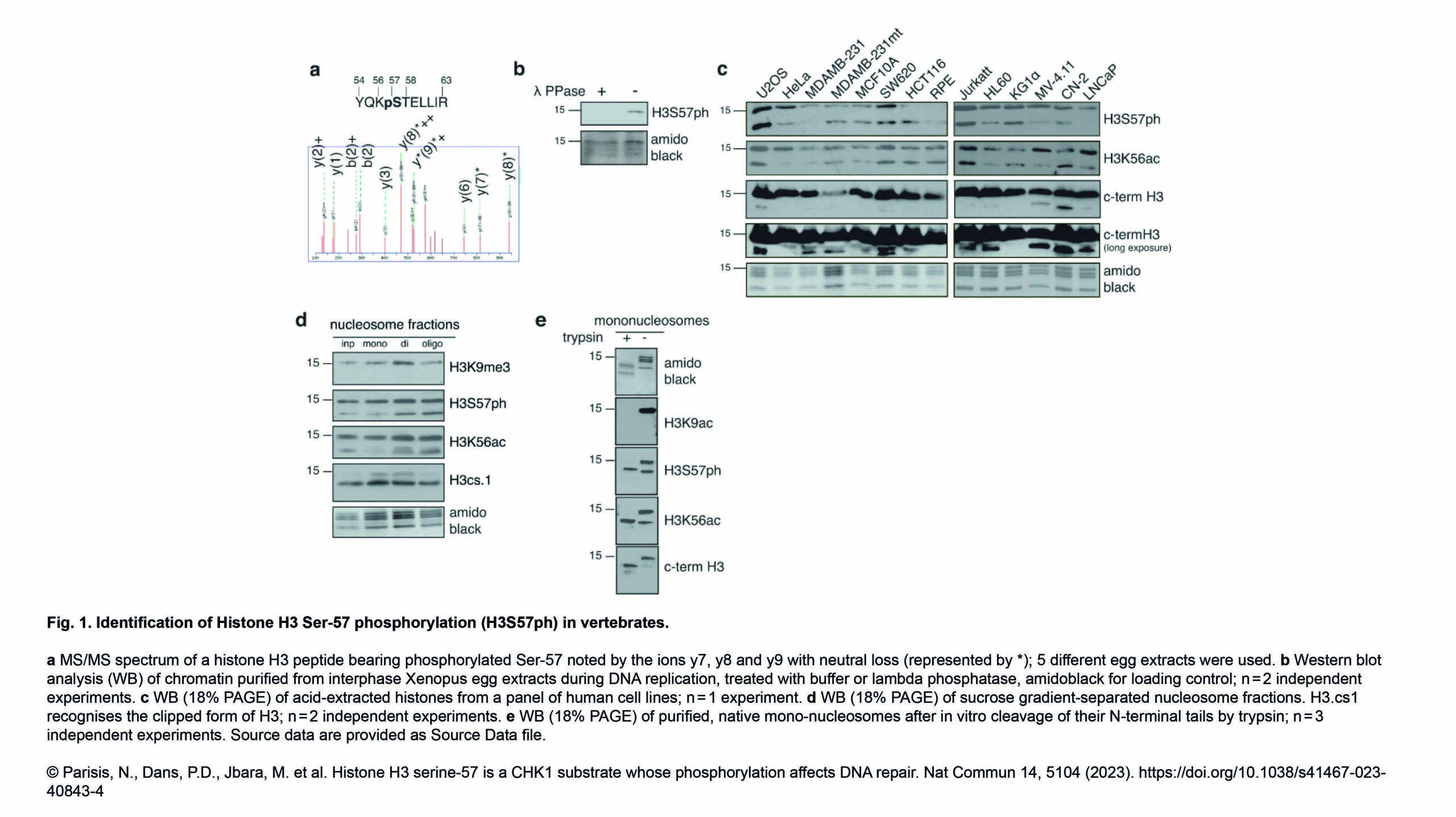
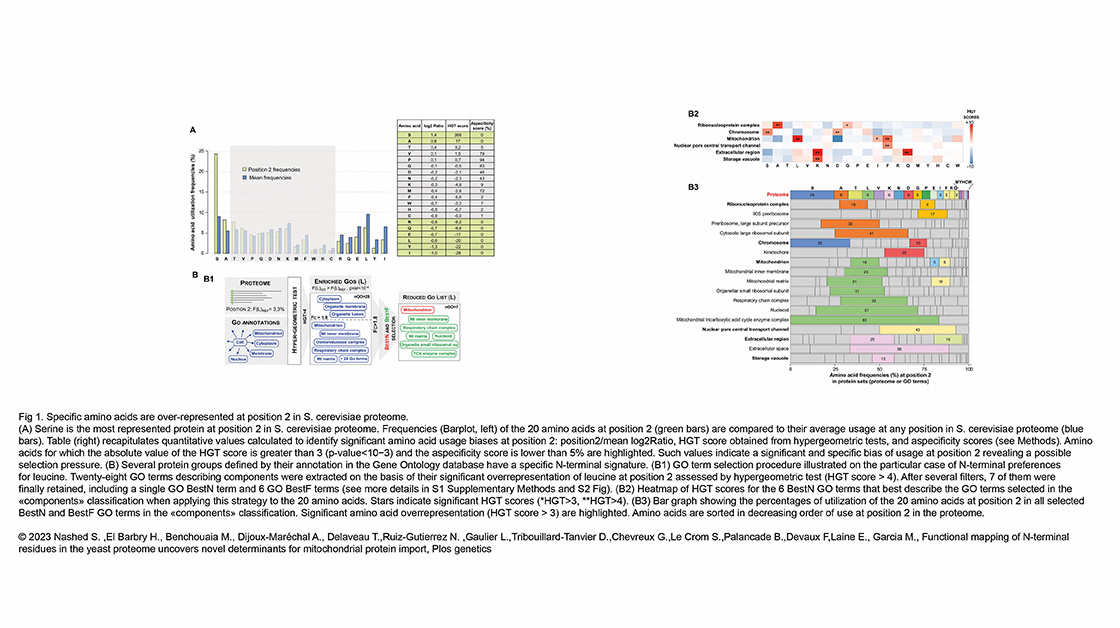
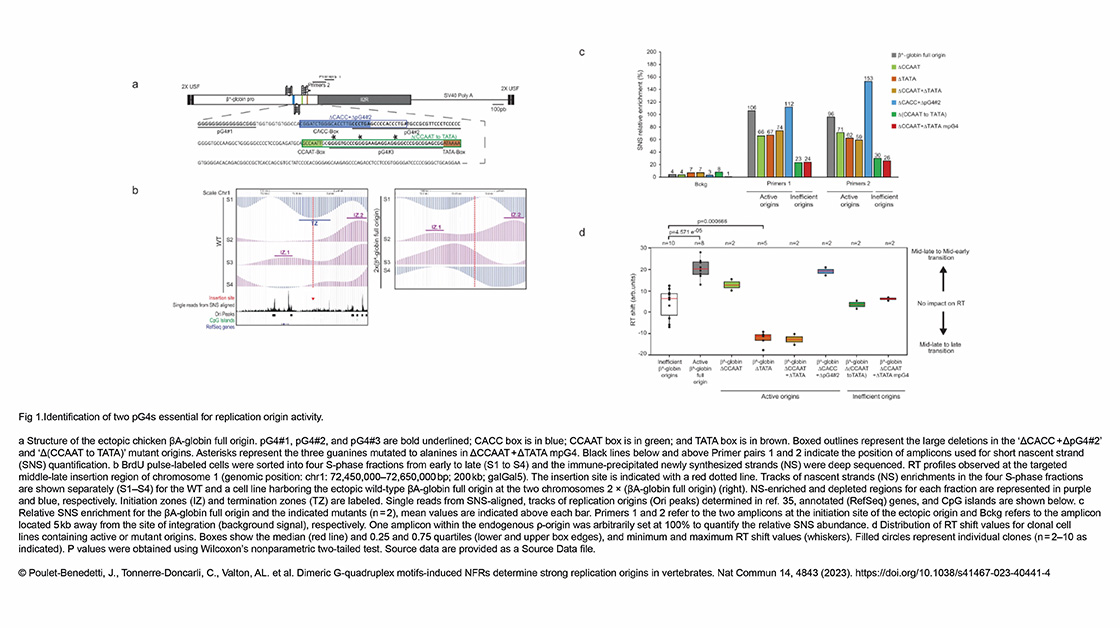
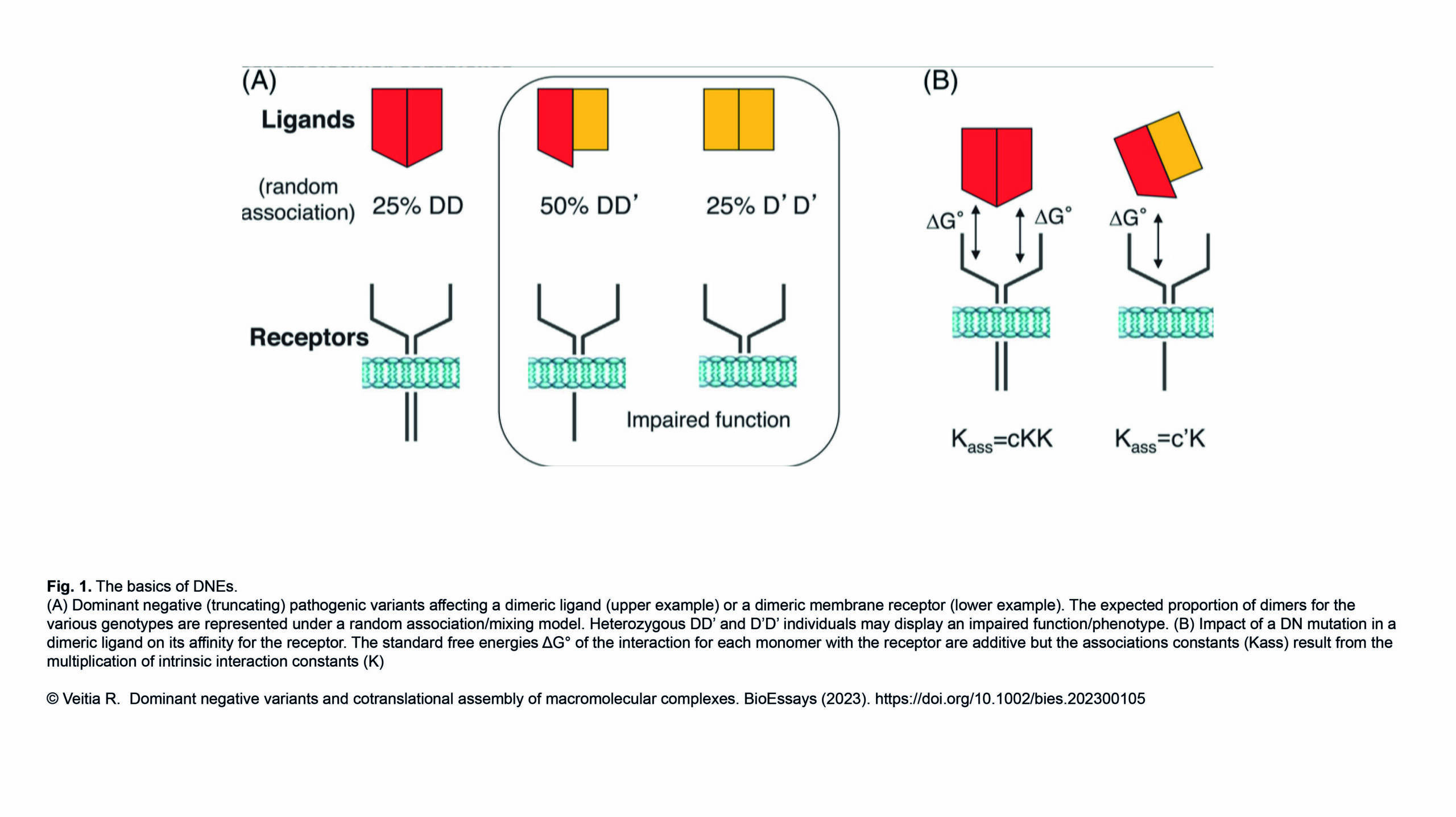
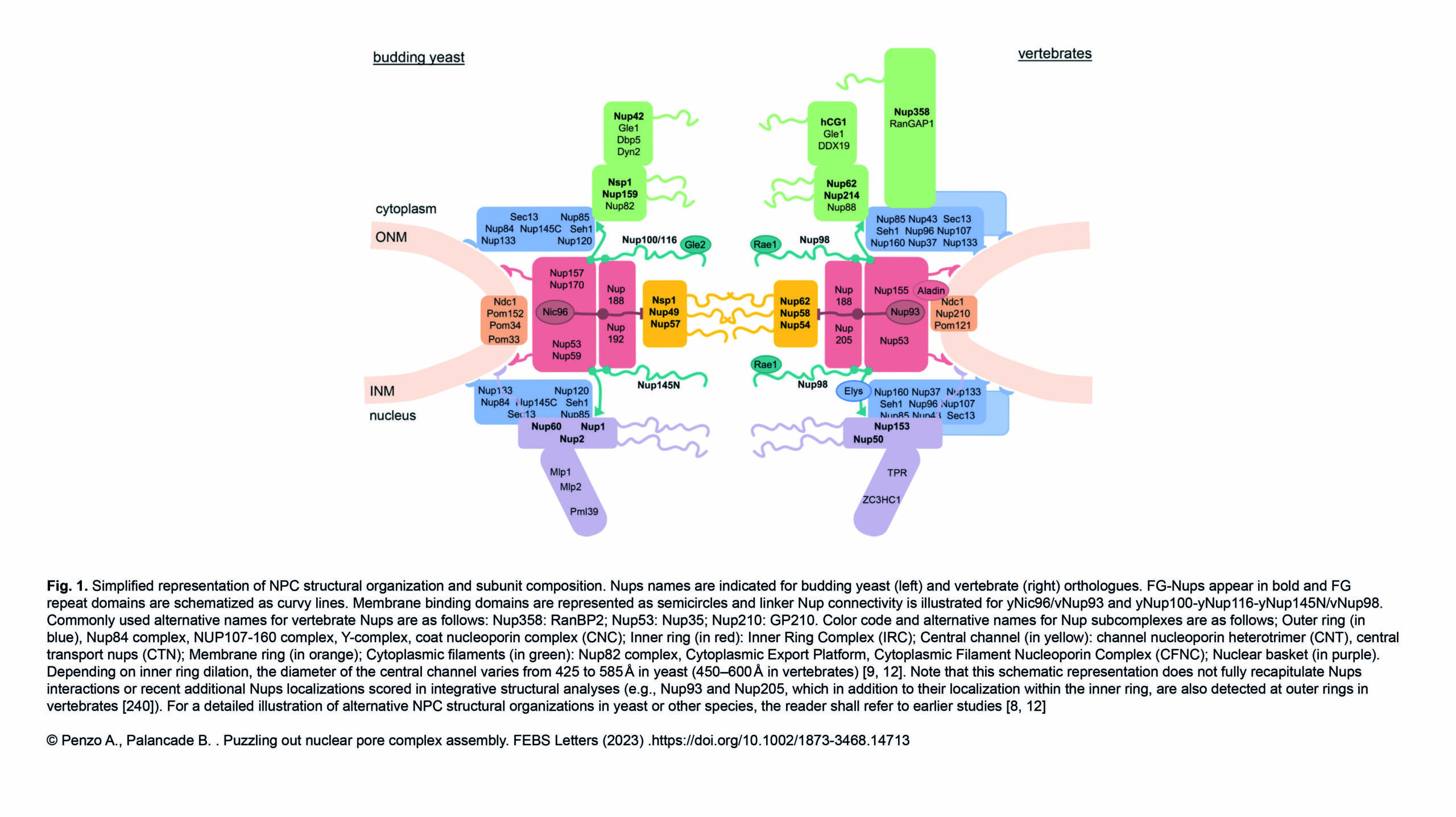
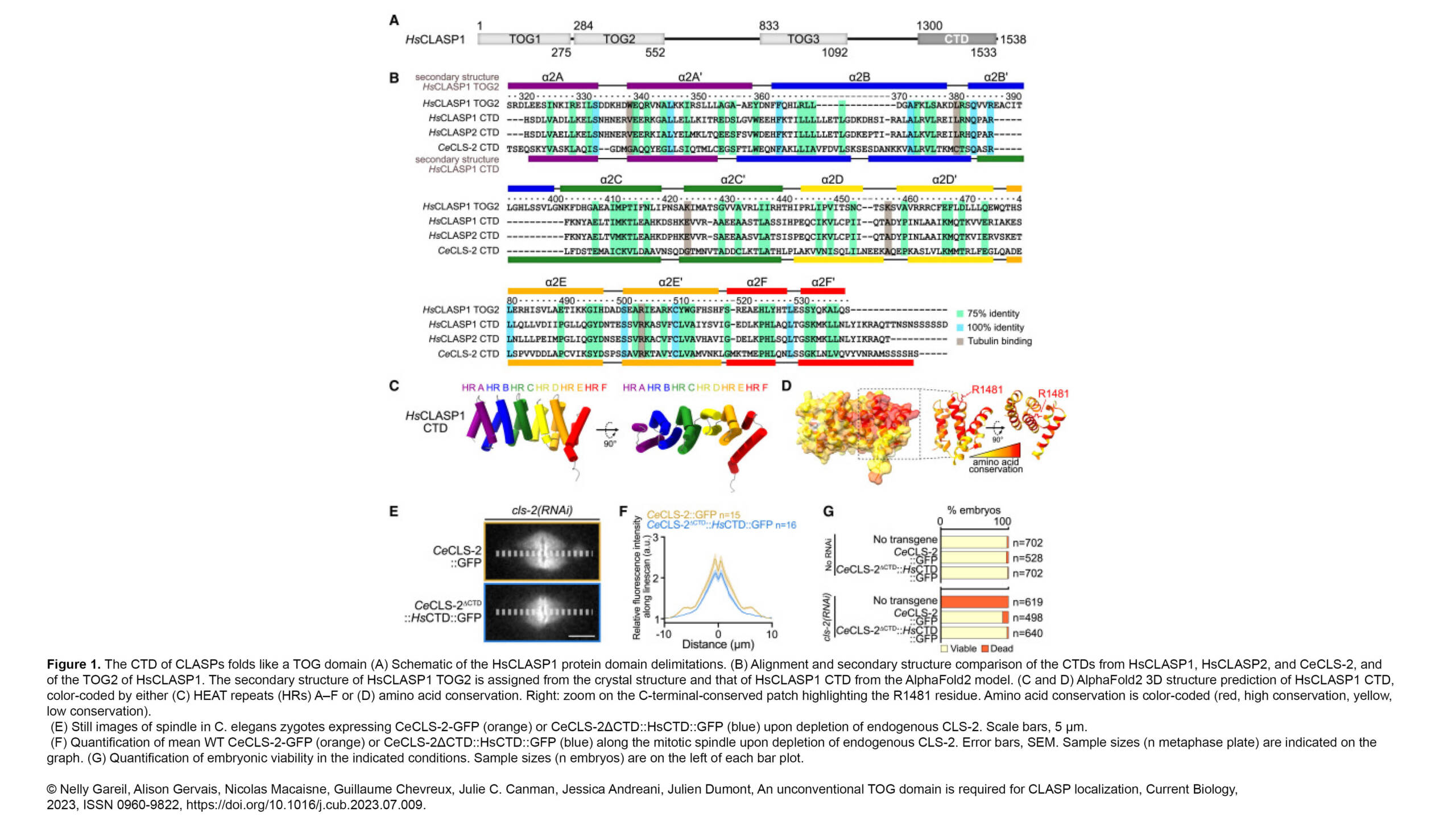
The Conduit Lab and the Guichet Lab recently published in Journal of Cell Biology :
Multifaceted modes of γ-tubulin complex recruitment and microtubule nucleation at mitotic centrosomes
Abstract:
Microtubule nucleation is mediated by γ-tubulin ring complexes (γ-TuRCs). In most eukaryotes, a GCP4/5/4/6 “core” complex promotes γ-tubulin small complex (γ-TuSC) association to generate cytosolic γ-TuRCs. Unlike γ-TuSCs, however,…