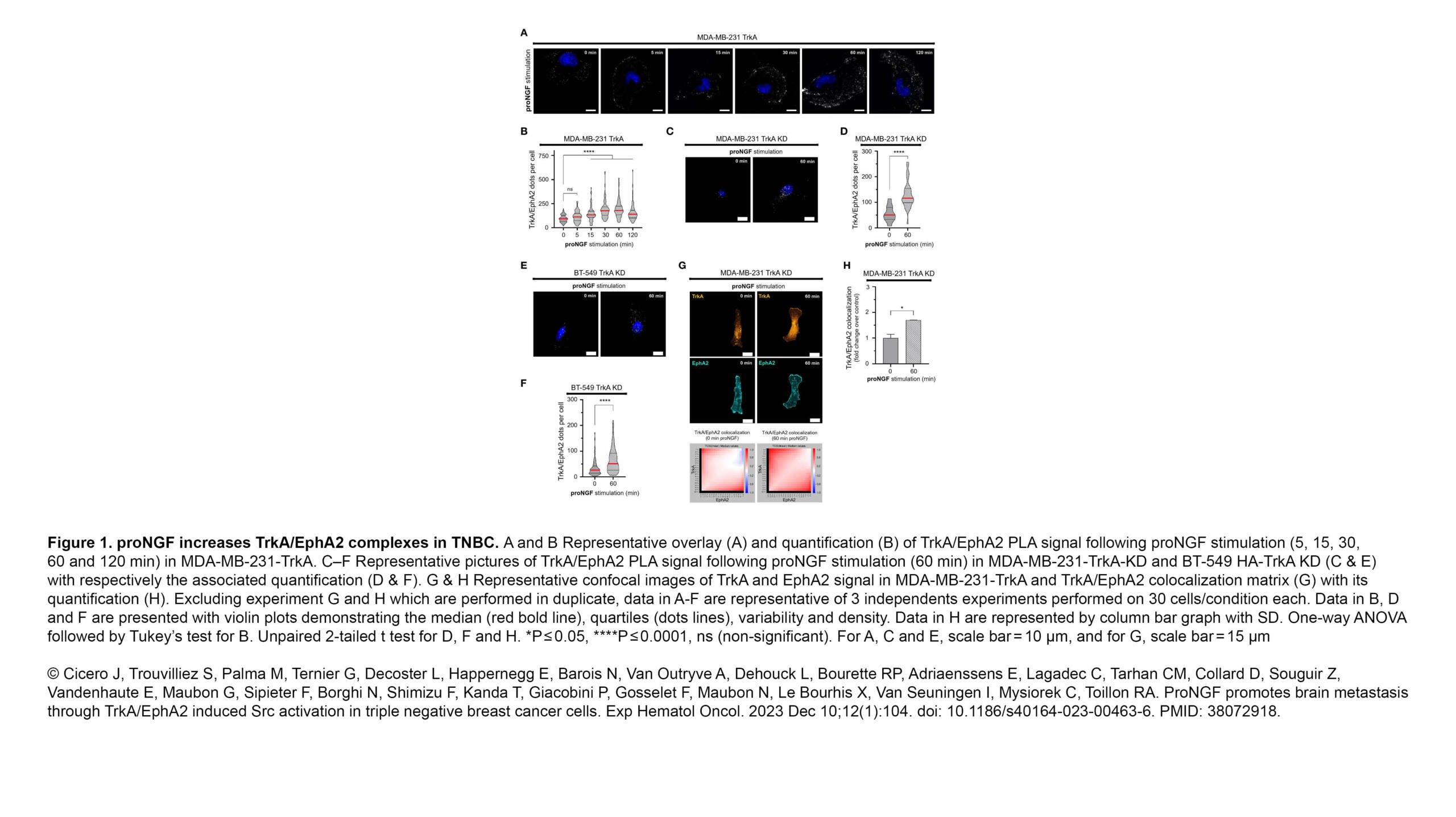
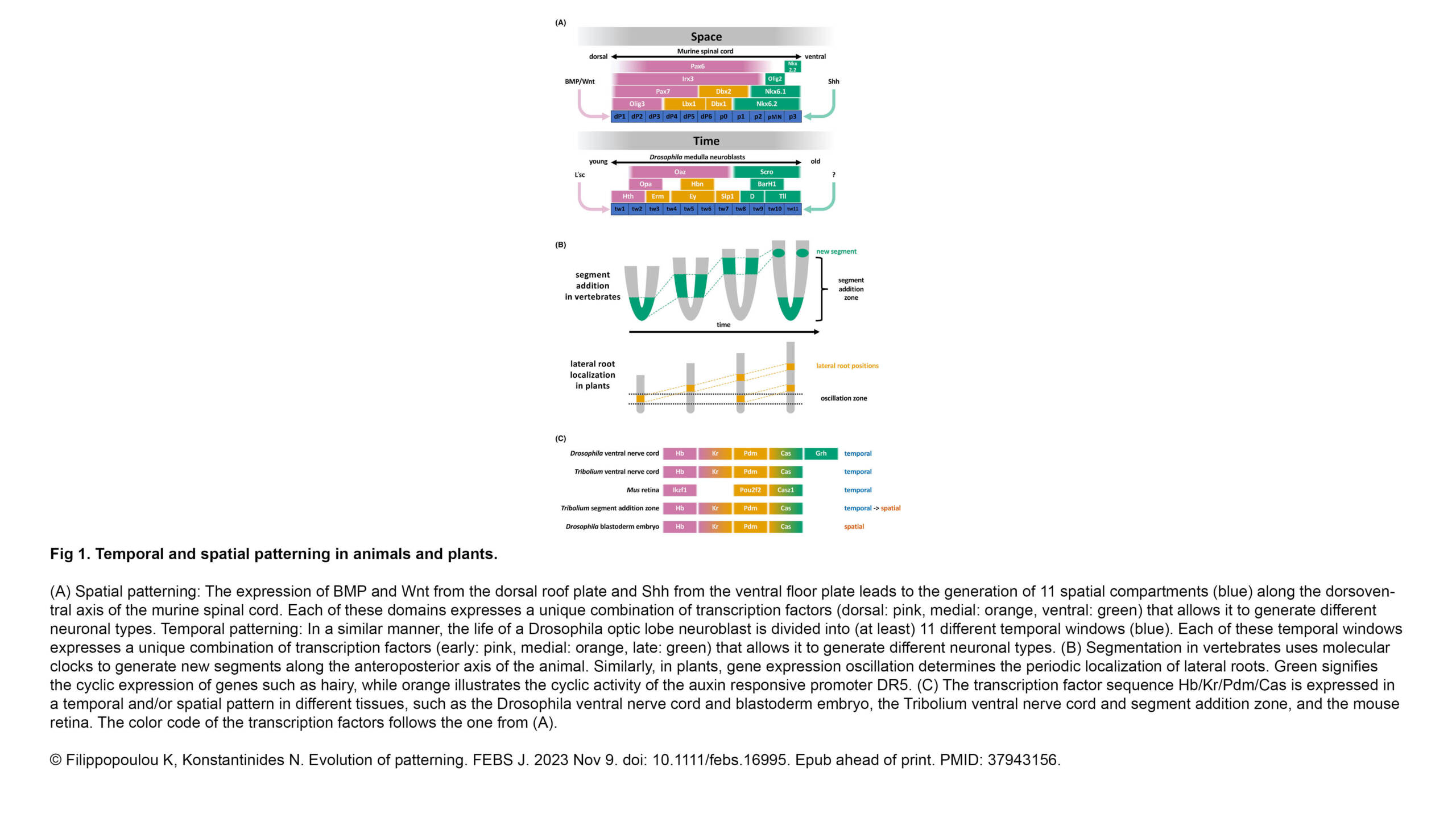
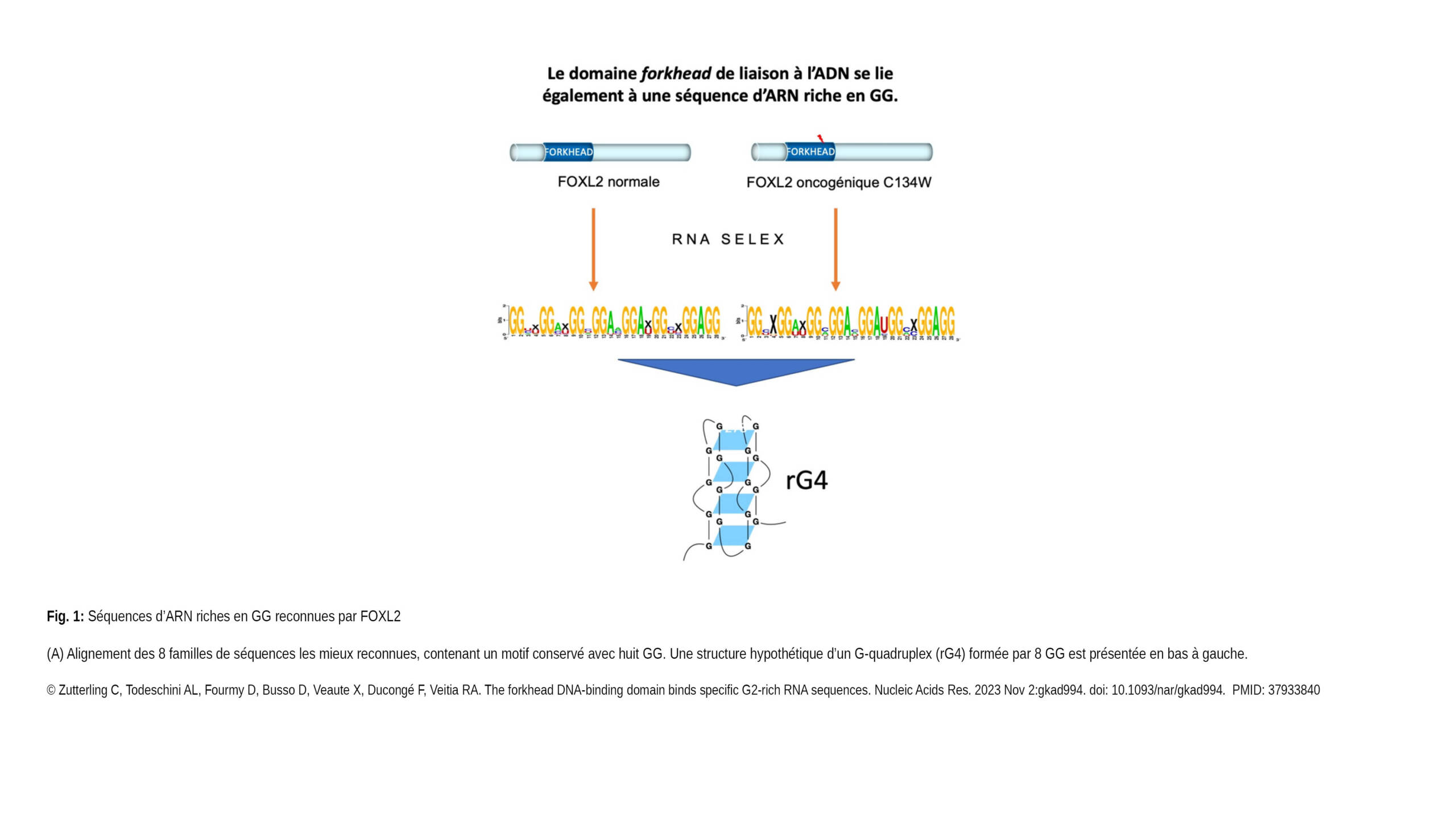
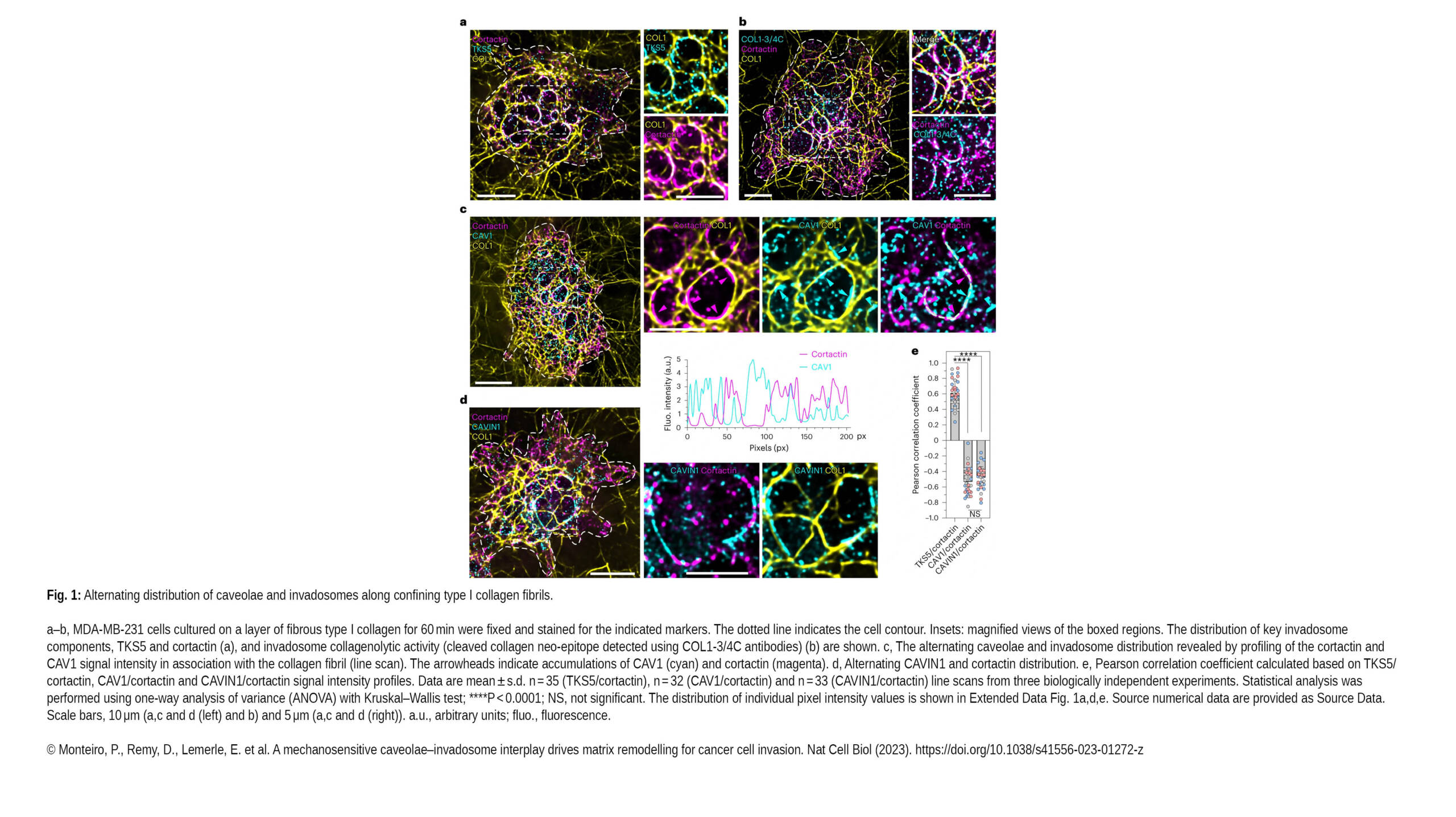
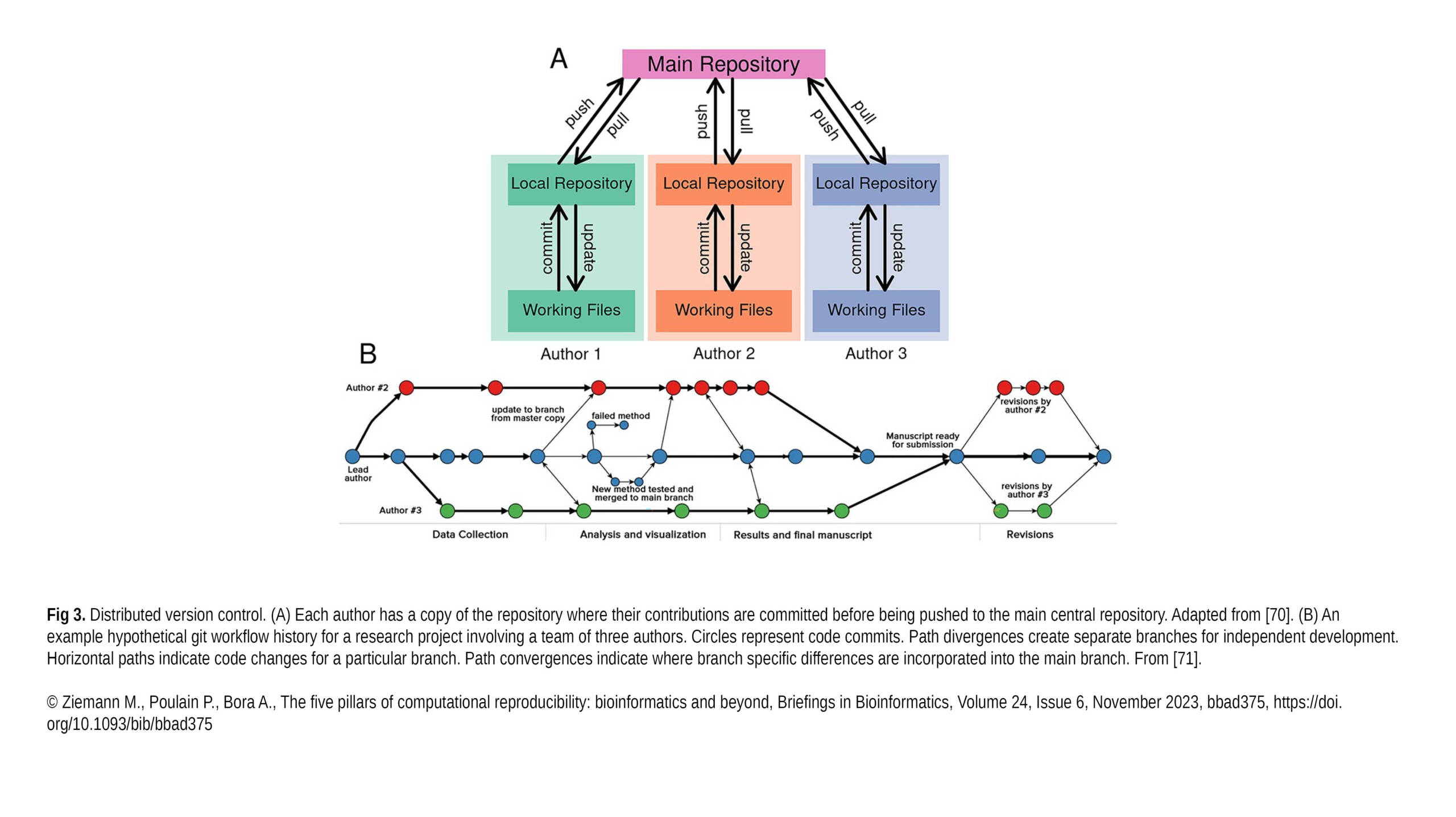
The Borghi Lab contributed to a new article published in Experimental Hematology & Oncology:
ProNGF promotes brain metastasis through TrkA/EphA2 induced Src activation in triple negative breast cancer cells
Abstract:
Background
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer is particularly aggressive, and its metastasis to the brain has a significant psychological impact on patients' quality of life, in addition to reducing…