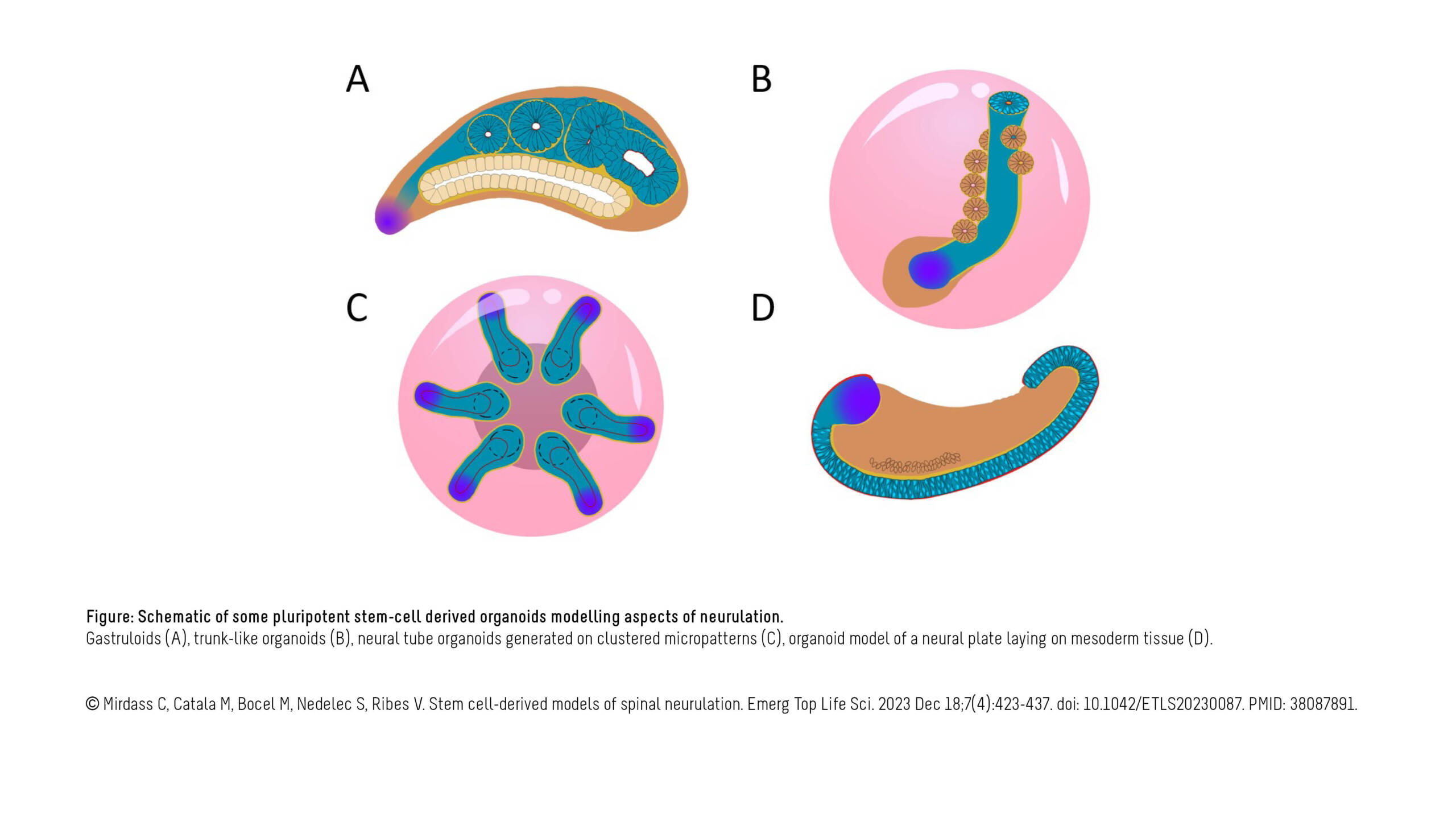
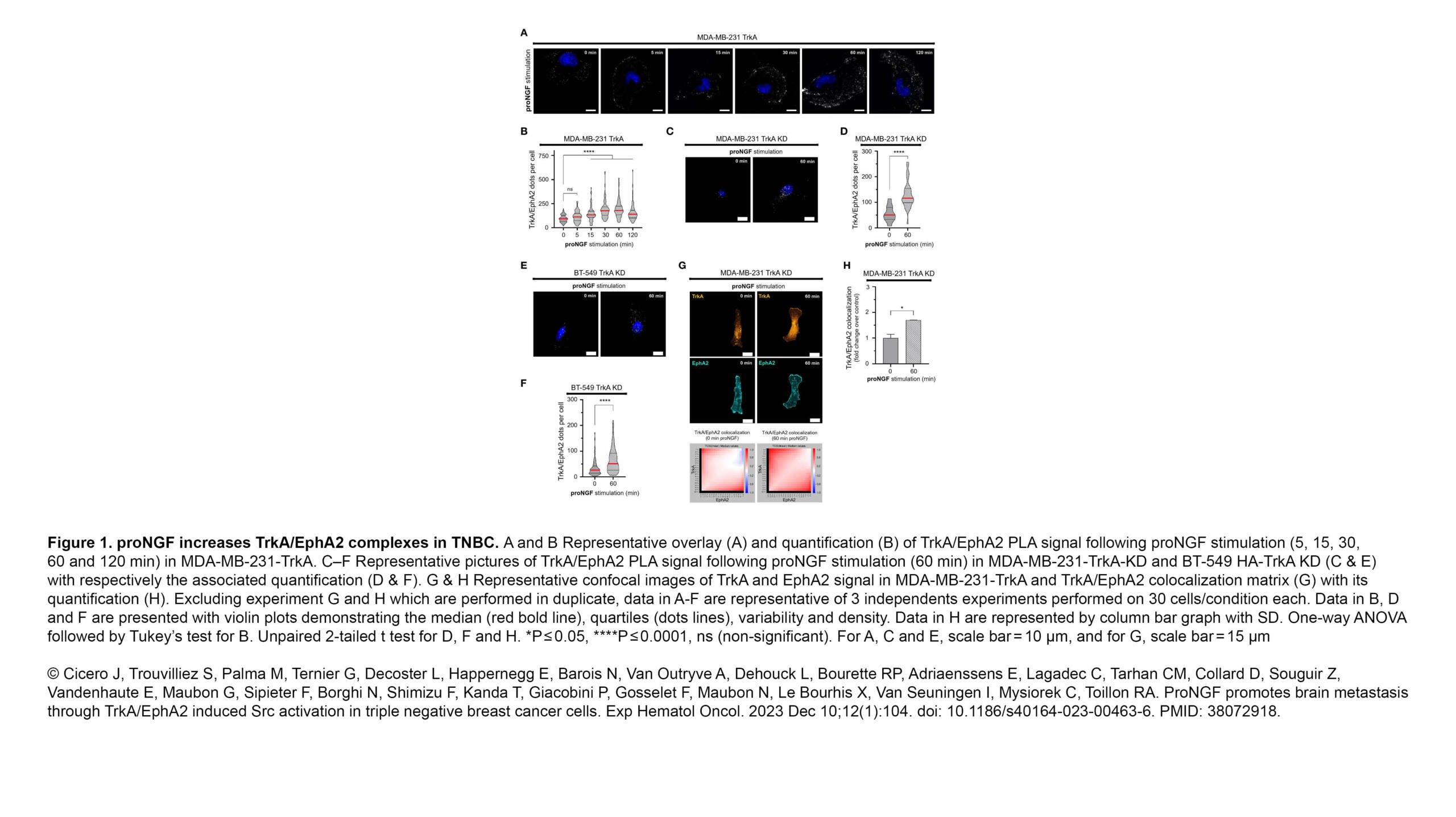
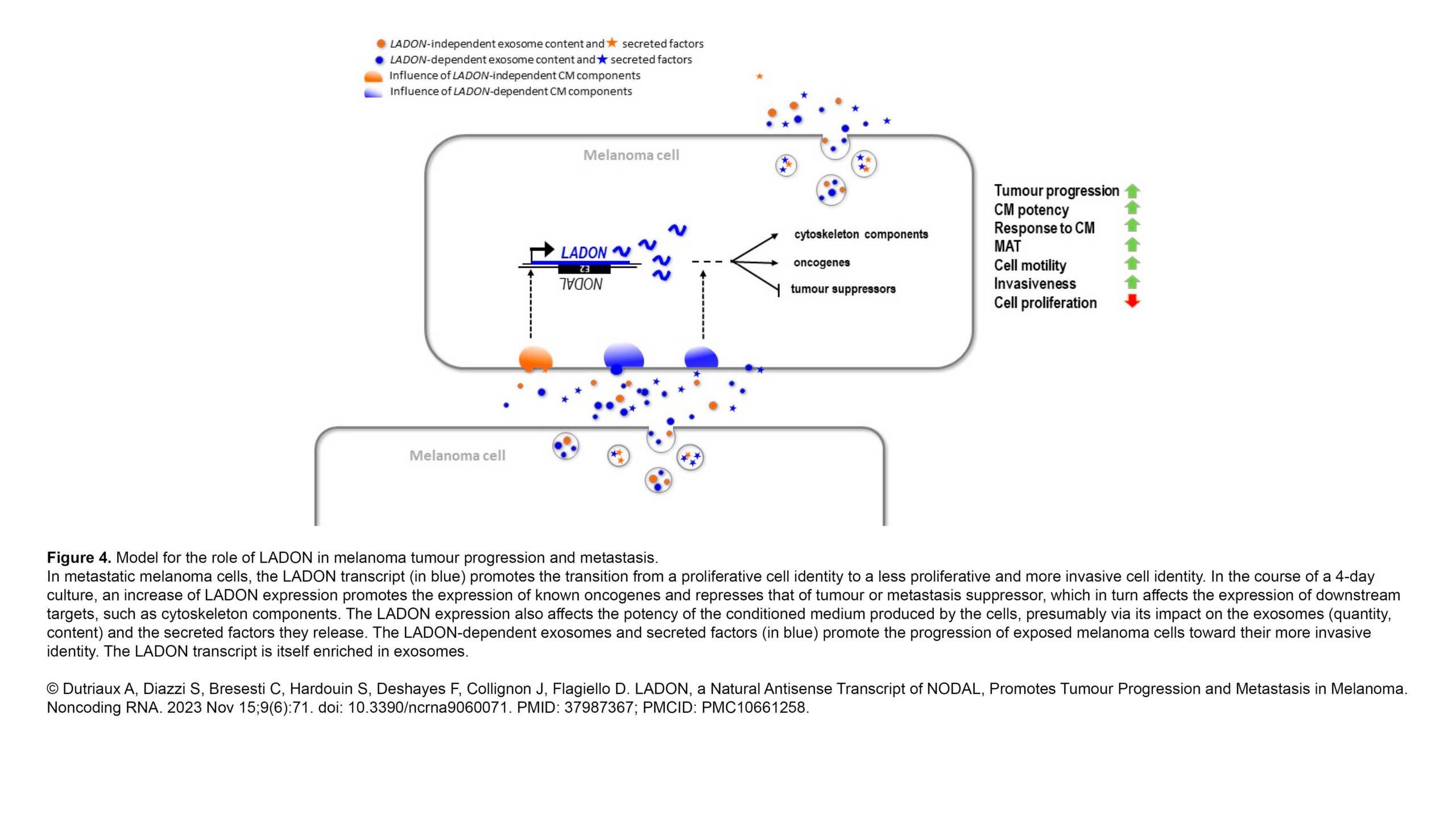
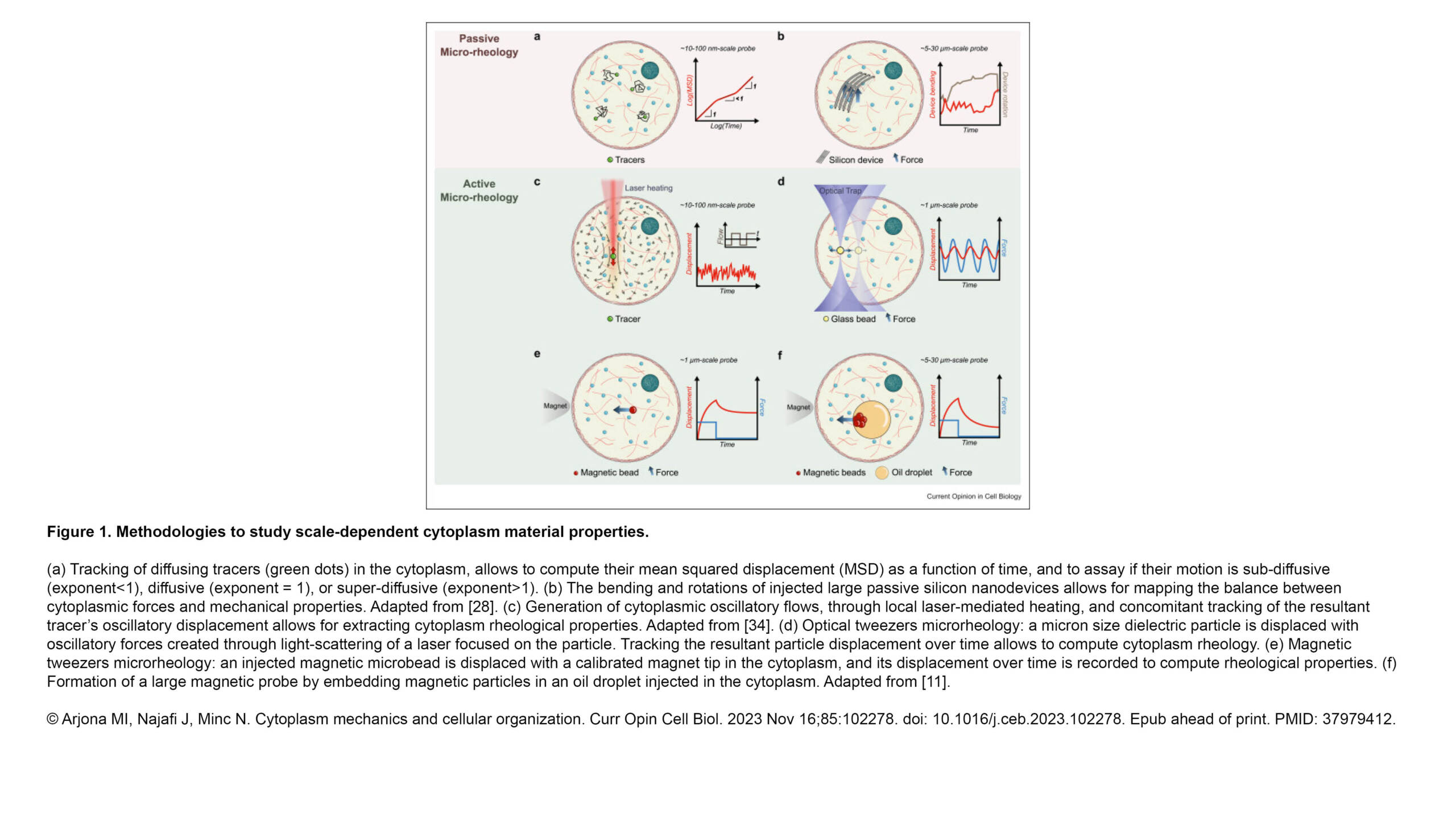
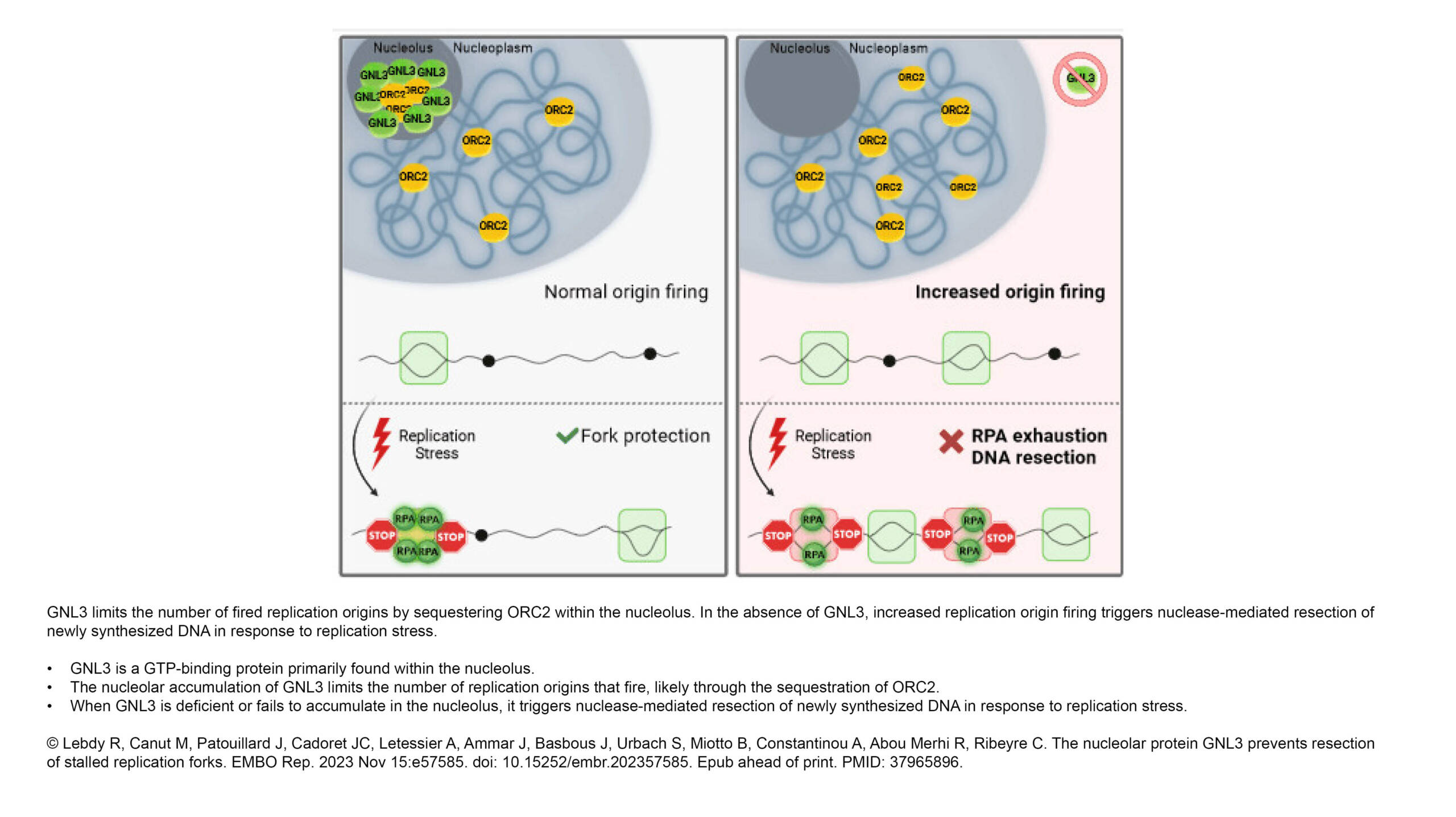
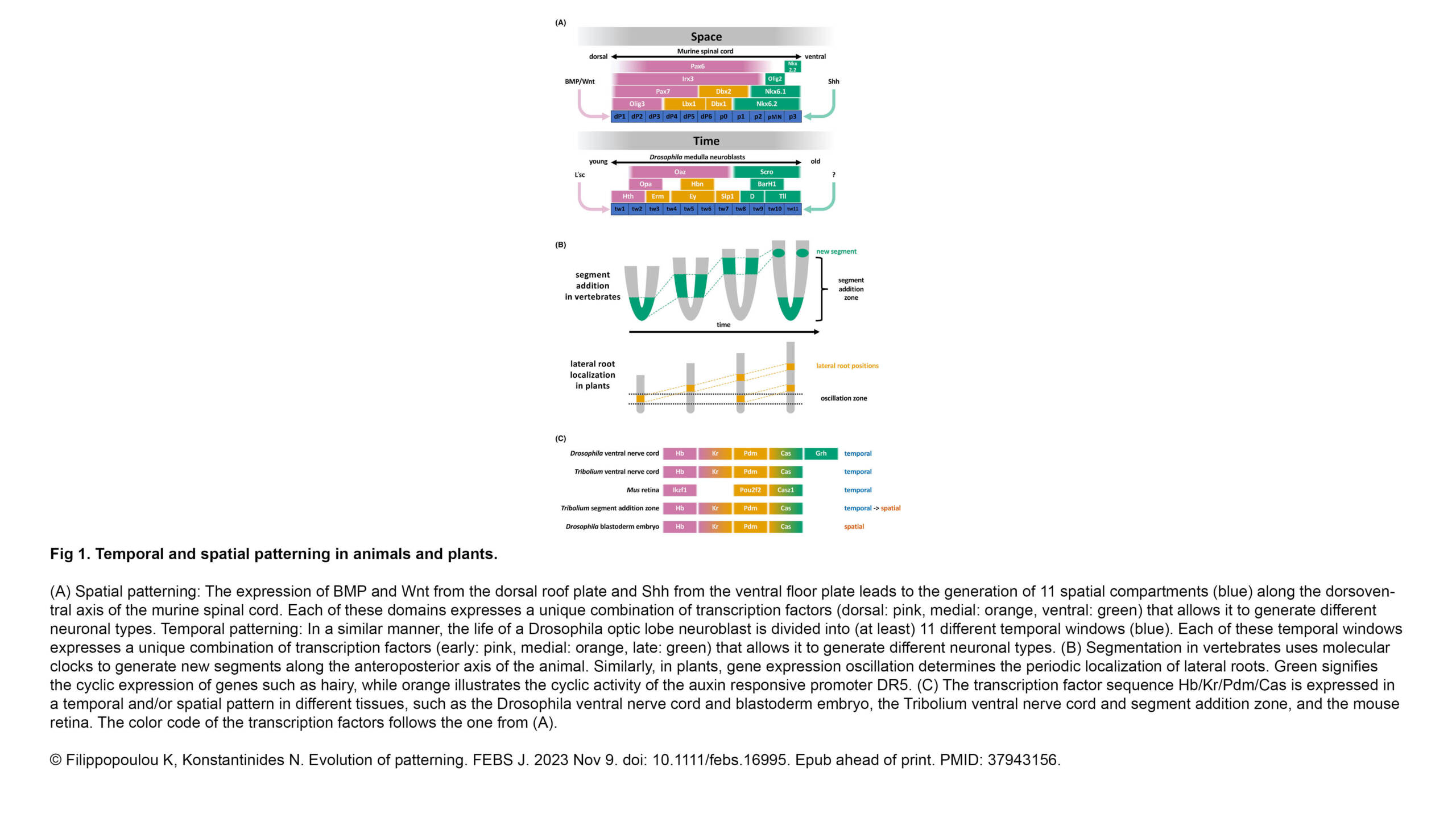
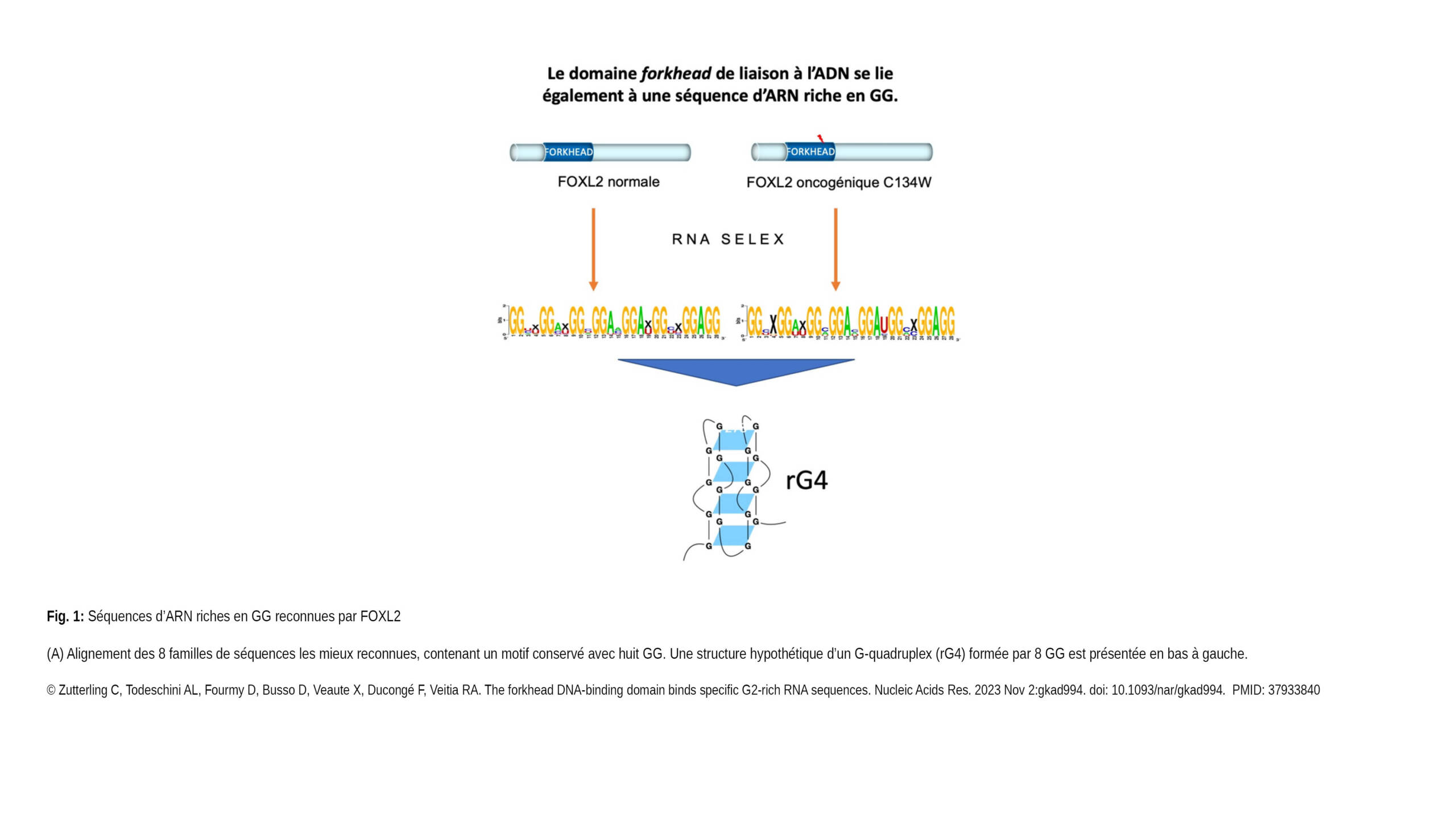
The Ribes Lab published a new article in Emerging topics in life sciences:
Stem cell-derived models of spinal neurulation
Abstract:
This review is the fruit of an enriching collaboration with my thesis supervisors Vanessa Ribes and Stéphane Nedelec (Institut du Fer à Moulin), along with Martin Catala (Institut de Biologie Paris Seine) and Mikaëlle Bocel (Institut Jacques…