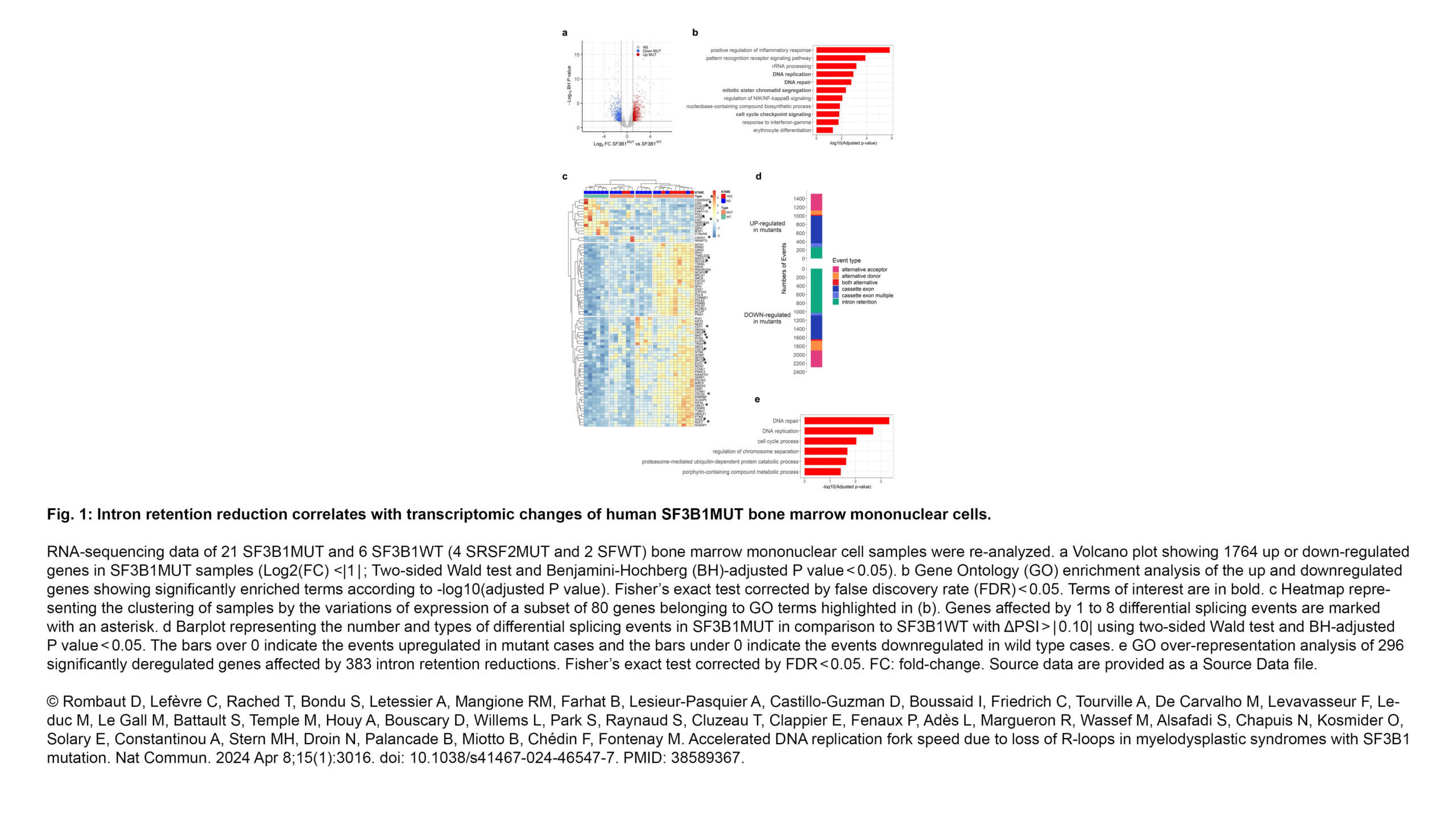
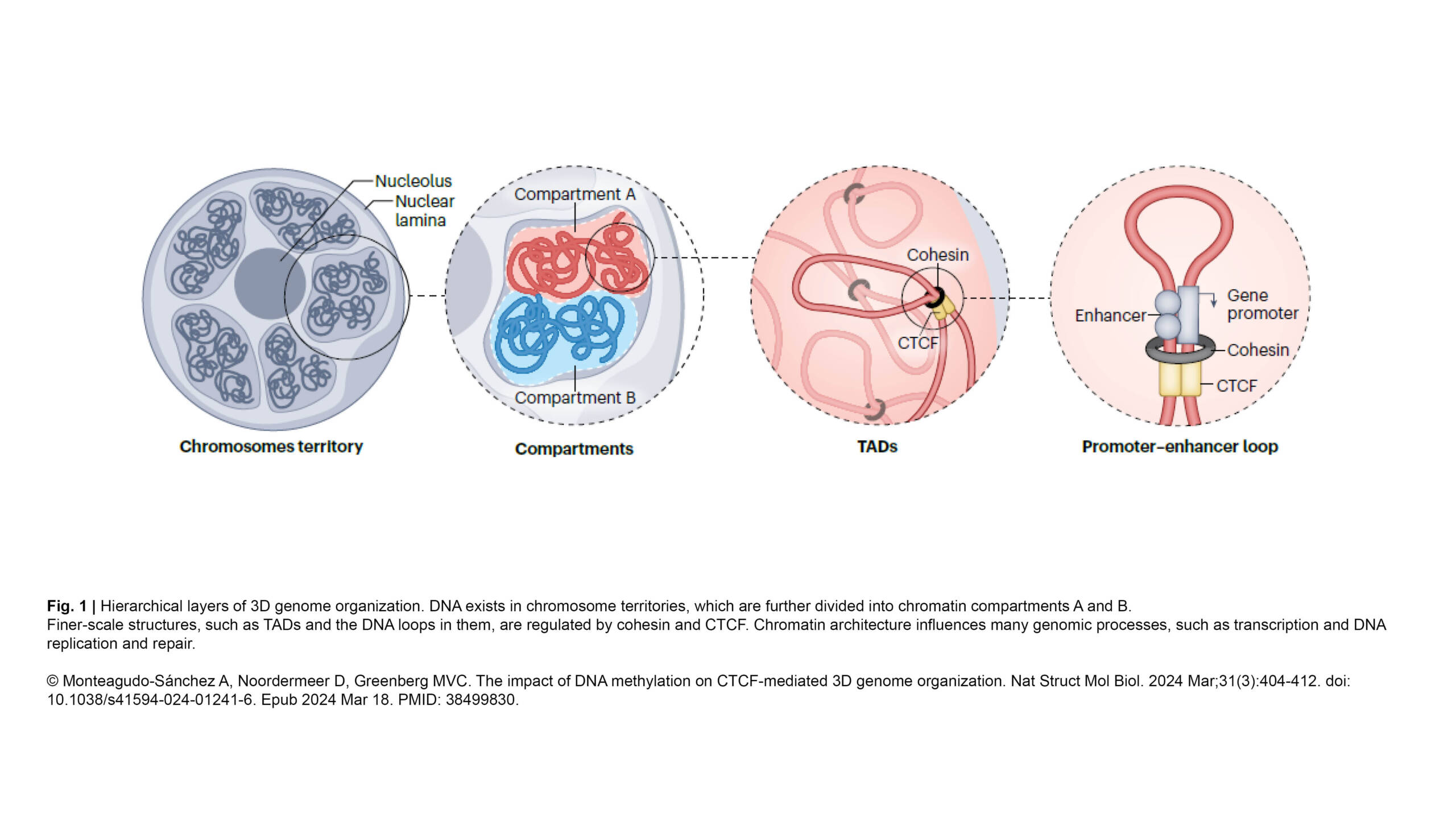
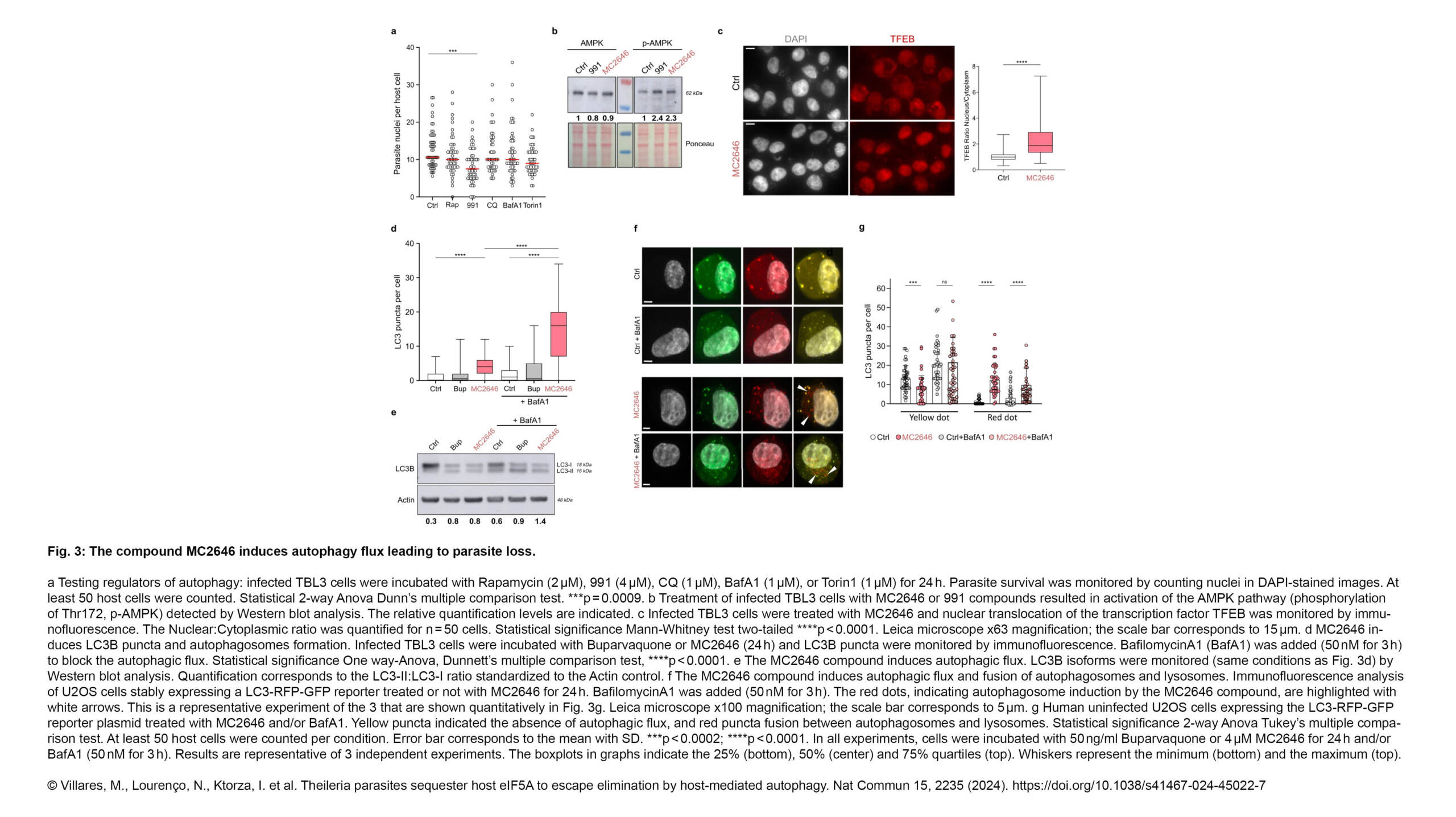
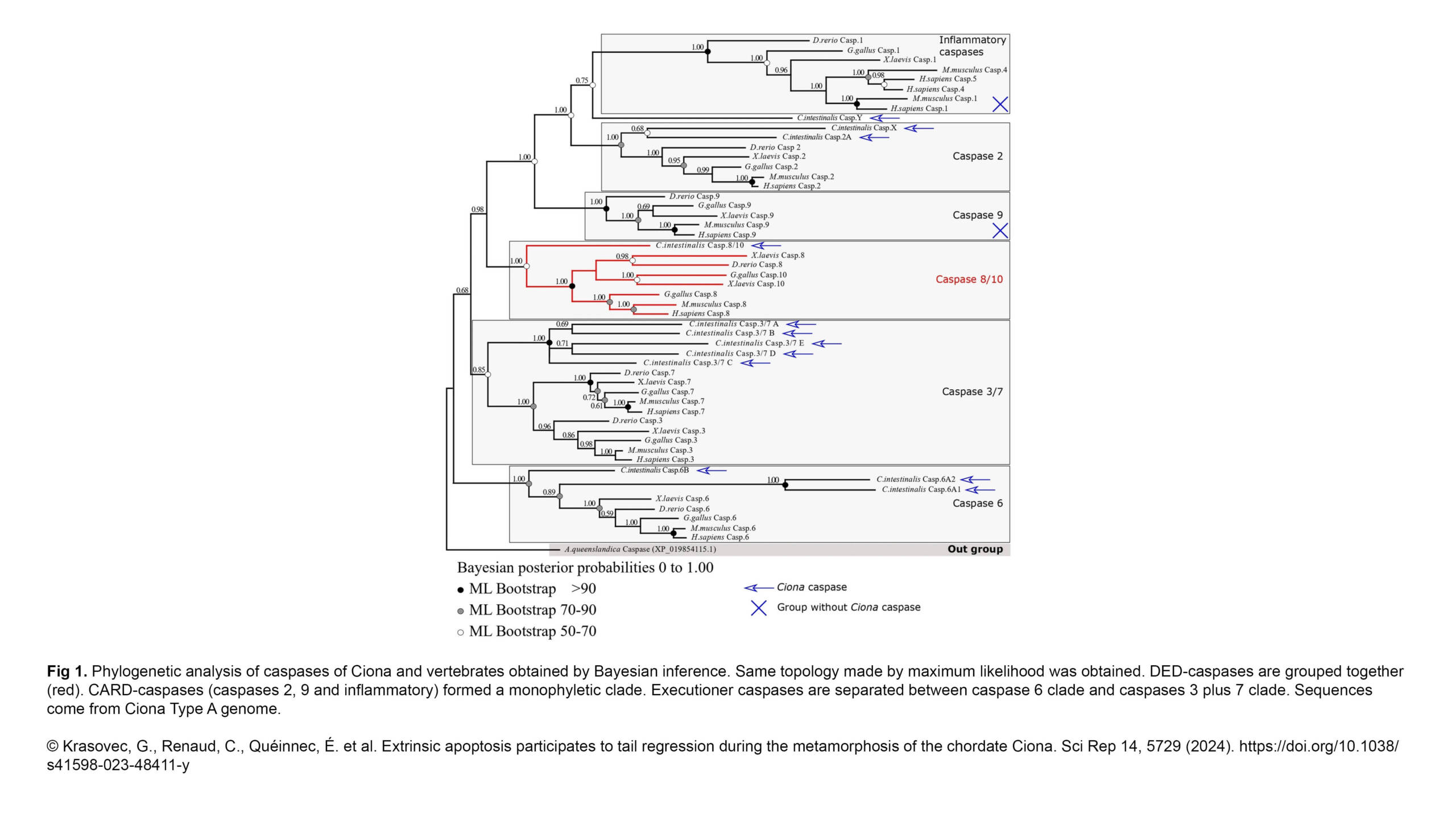
The next Cytoskeleton Club meeting will take place on Wednesday, May 15th at the Institut Jacques Monod:
Rose Bulteau (PhD student, Verlhac/Terret Lab, CIRB Collège de France) will present "Mechanical characterization of oocytes using Atomic Force Microscopy to evaluate their developmental potential".
Coralie Fassier (co-director of the Nicol/Fassier Lab, « Institut de la vison.…