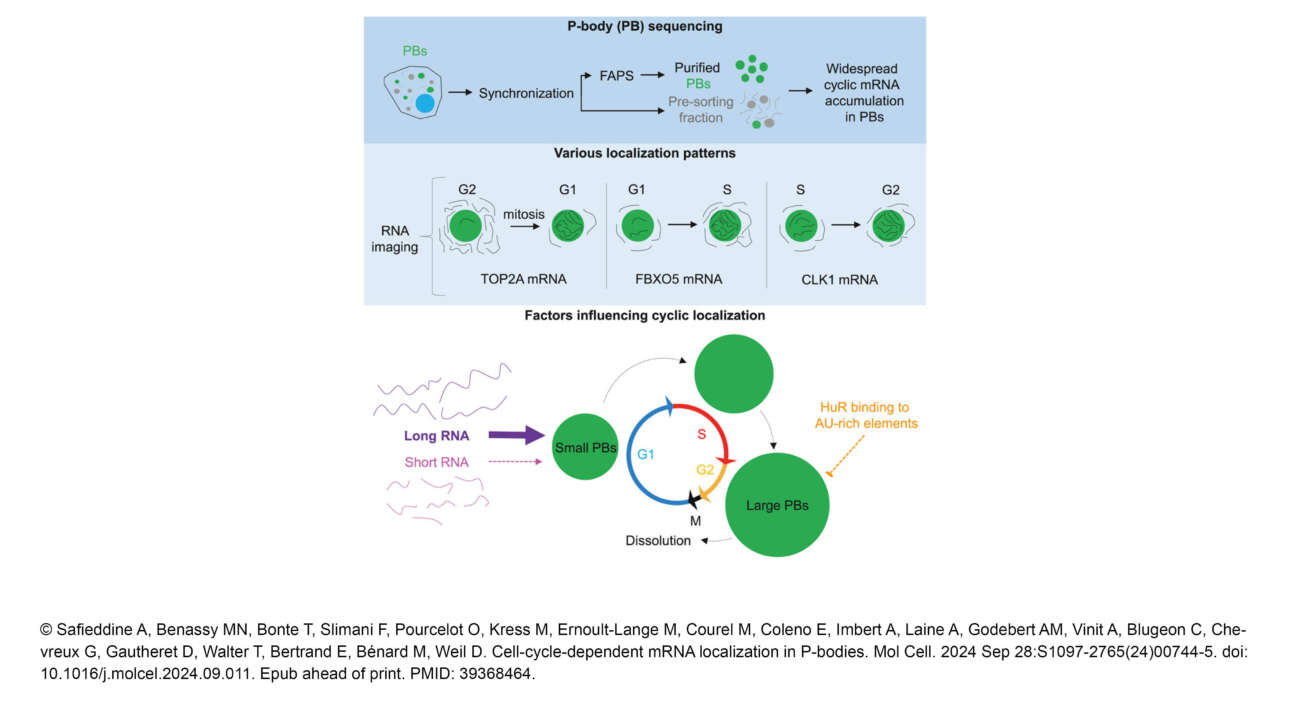
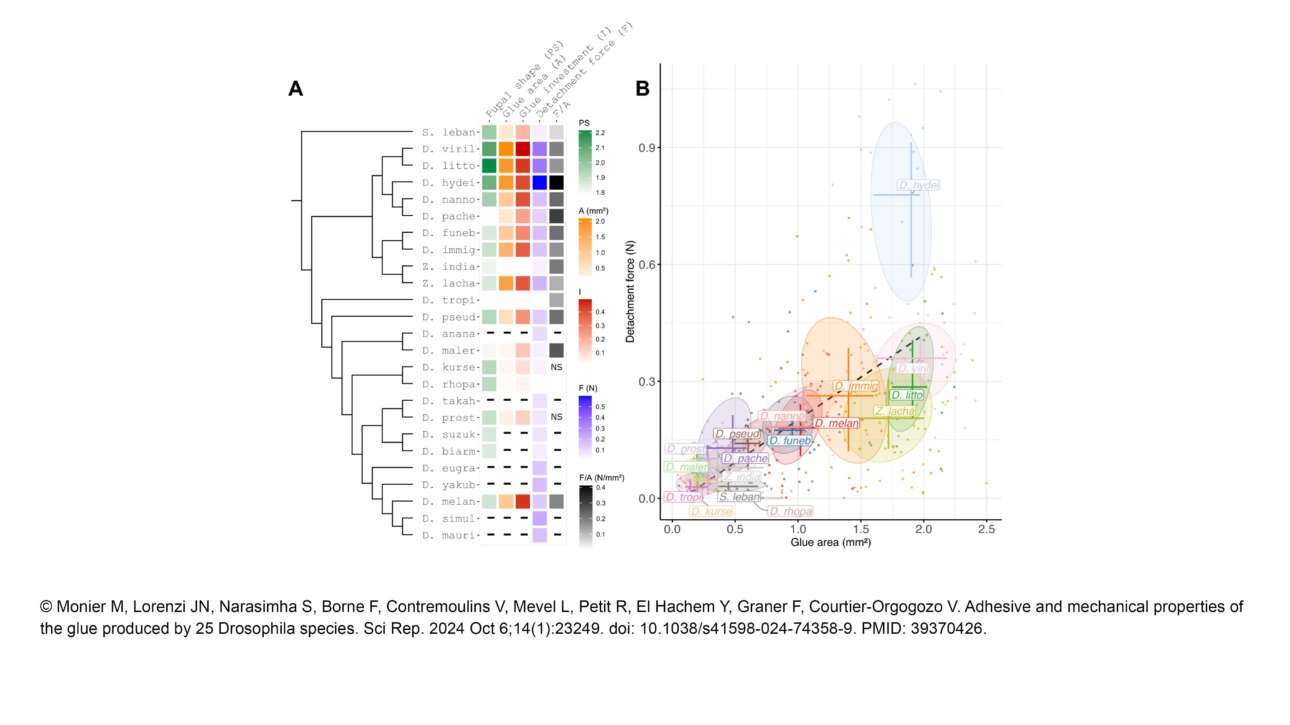
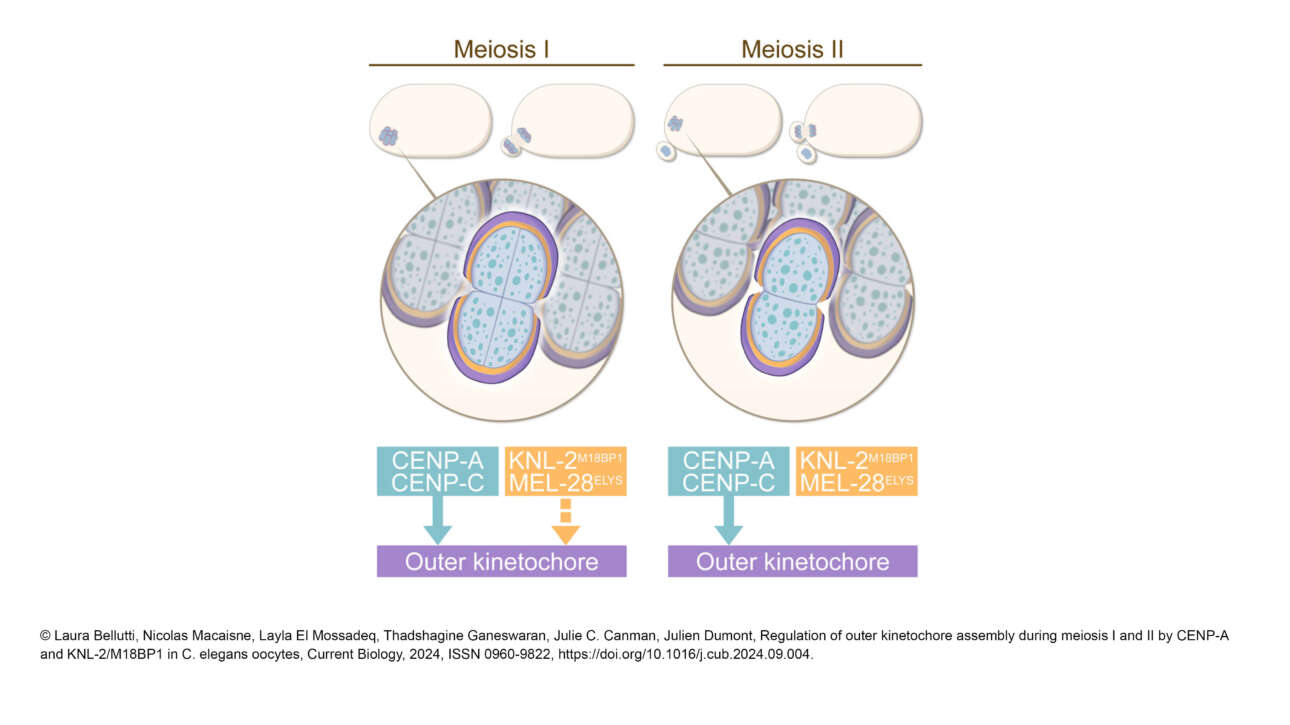
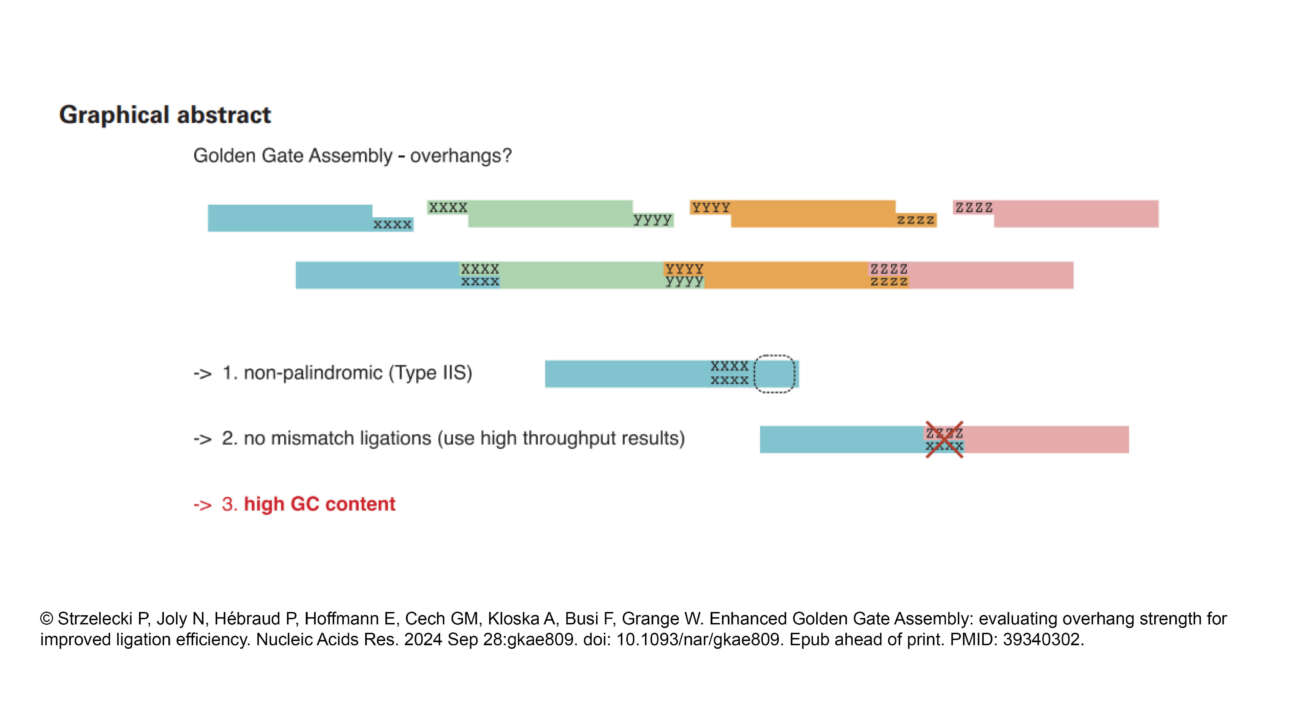
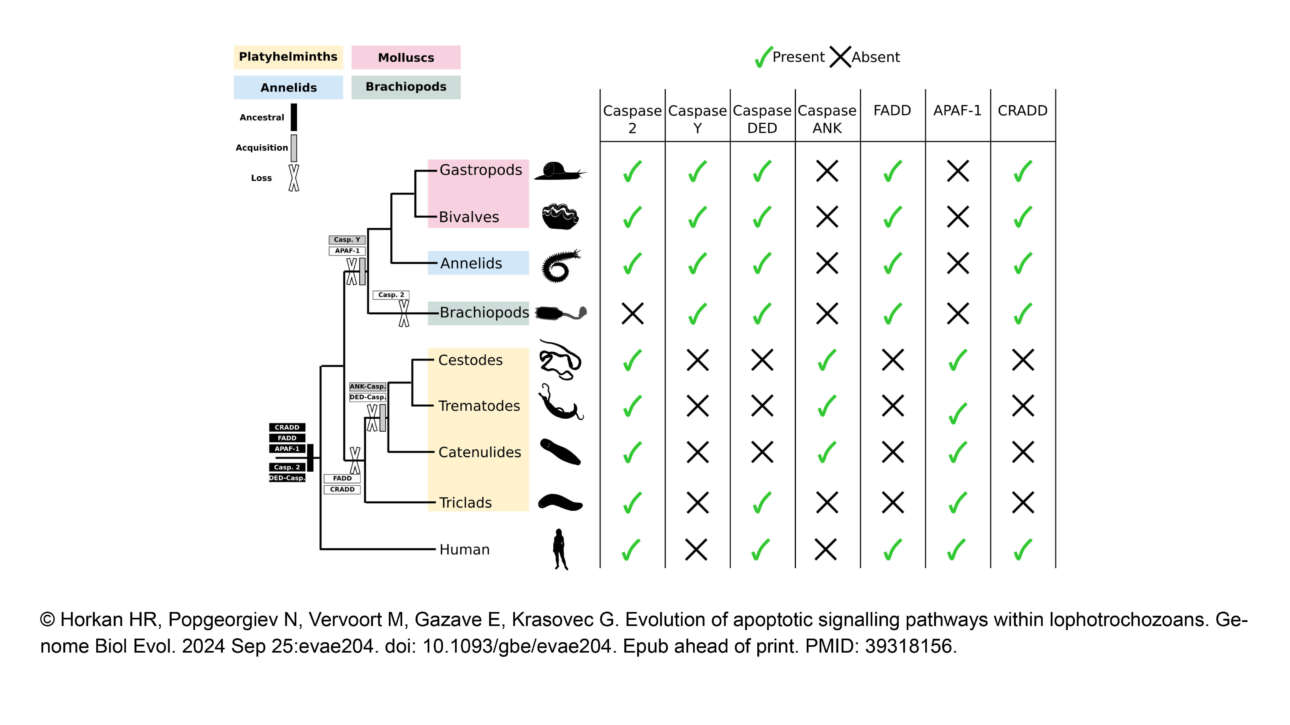
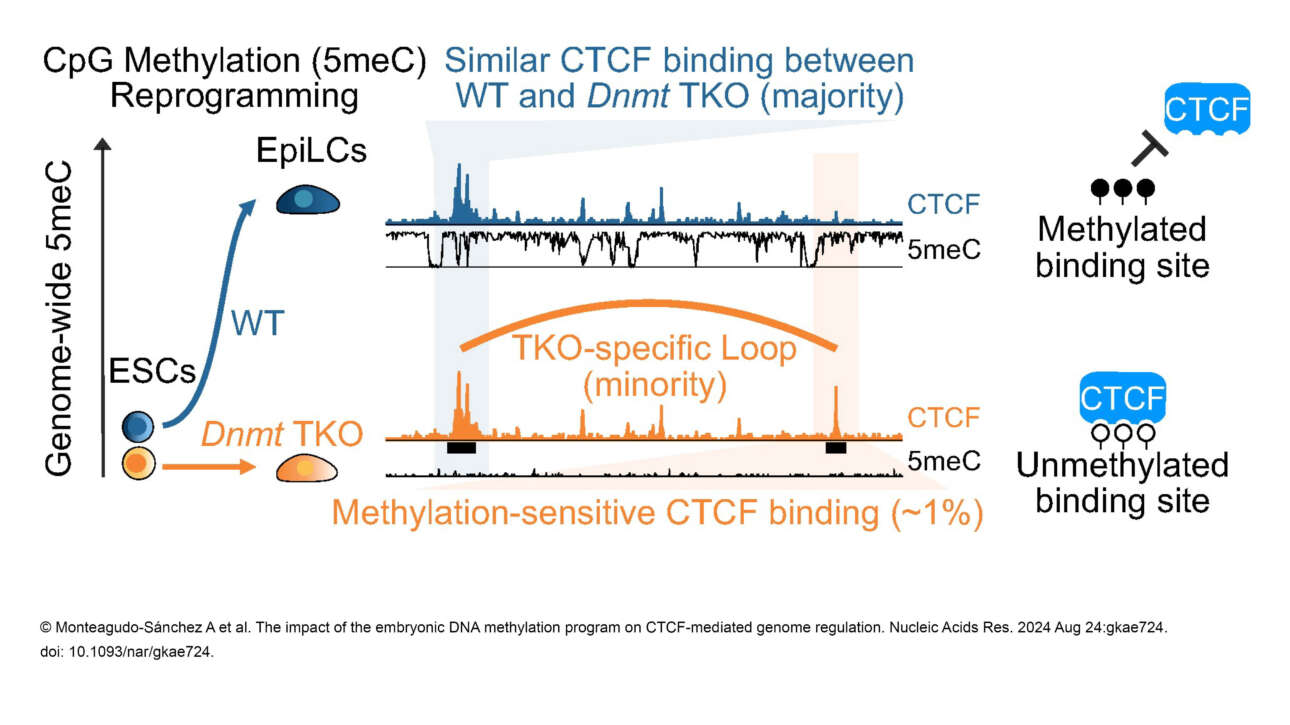
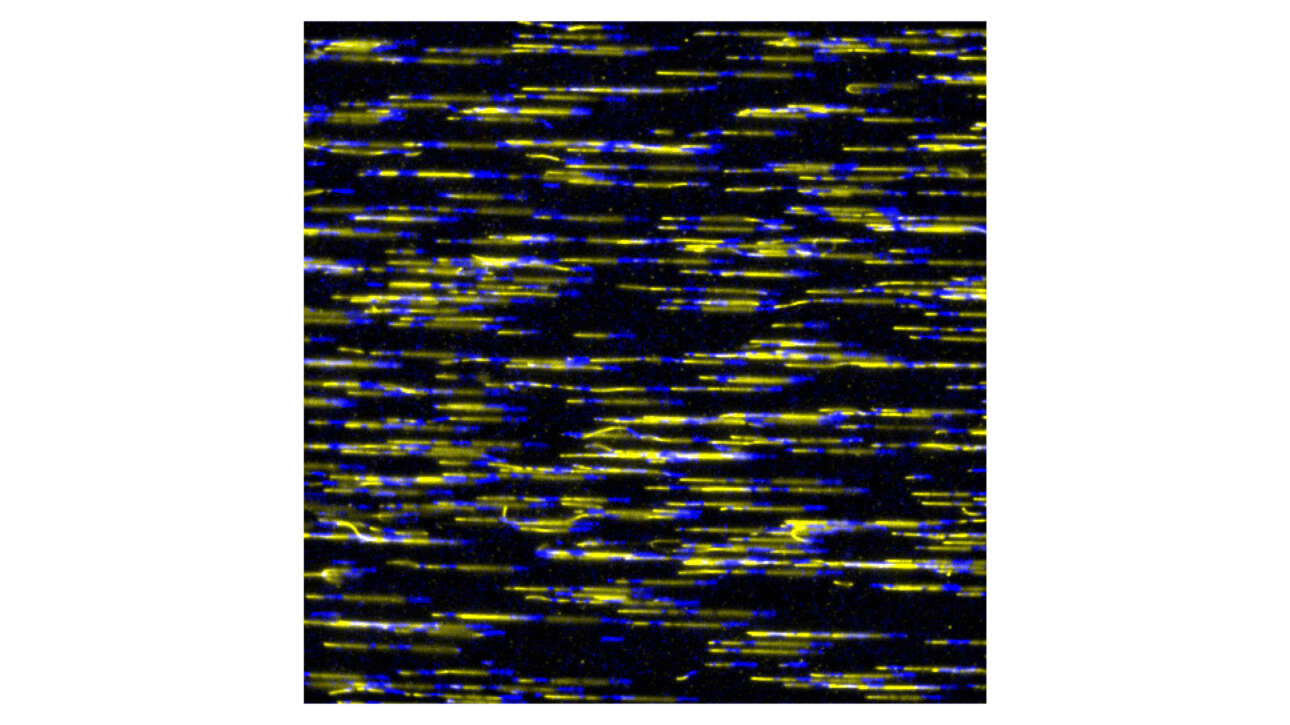
The Ribes lab published a new article in Elife:
BMP2 and BMP7 cooperate with H3.3K27M to promote quiescence and invasiveness in pediatric diffuse midline gliomas
Abstract:
Pediatric diffuse midline gliomas (pDMG) are an aggressive type of childhood cancer with a fatal outcome. Their major epigenetic determinism has become clear, notably with the identification of K27M mutations in…