General information
Offer title : postdoctoral researcher in computational and experimental biology M/F (H/F)
Reference : UMR7592-SANDUH-011
Number of position : 1
Workplace : PARIS 13
Date of publication : 23 January 2026
Type of Contract : Researcher in FTC
Contract Period : 3 months
Expected date of employment : 1 April 2026
Proportion of work : Full Time
Remuneration : 3100 euros brut
Desired level of education : Doctorate
Experience required : 1…
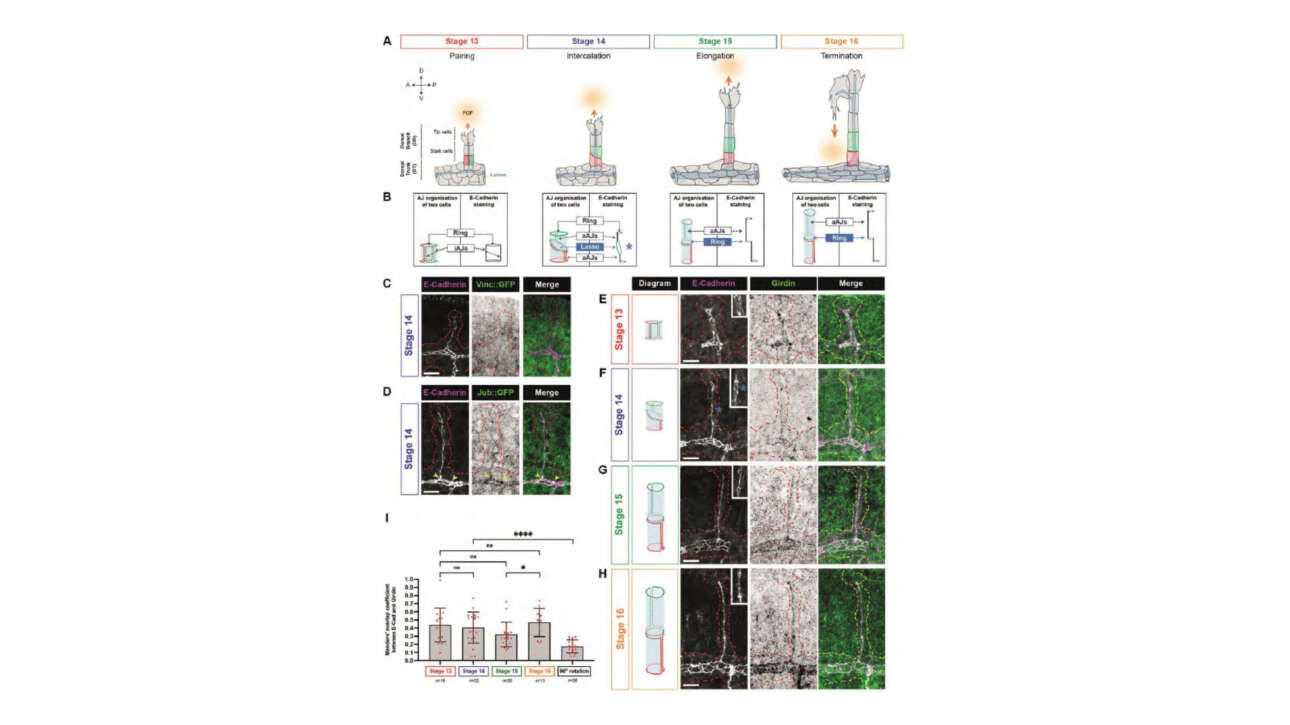
The Guichet Lab published a new article in Development:
Girdin controls the pace of 3D tracheal cell intercalation by coupling adherens junctions to the actin cytoskeleton in Drosophila
Abstract:
Morphogenesis is orchestrated through coordinated cell movements, including cell intercalation, which drives extensive changes in cell shape and position. This process requires precise regulation of interactions between Adherens…

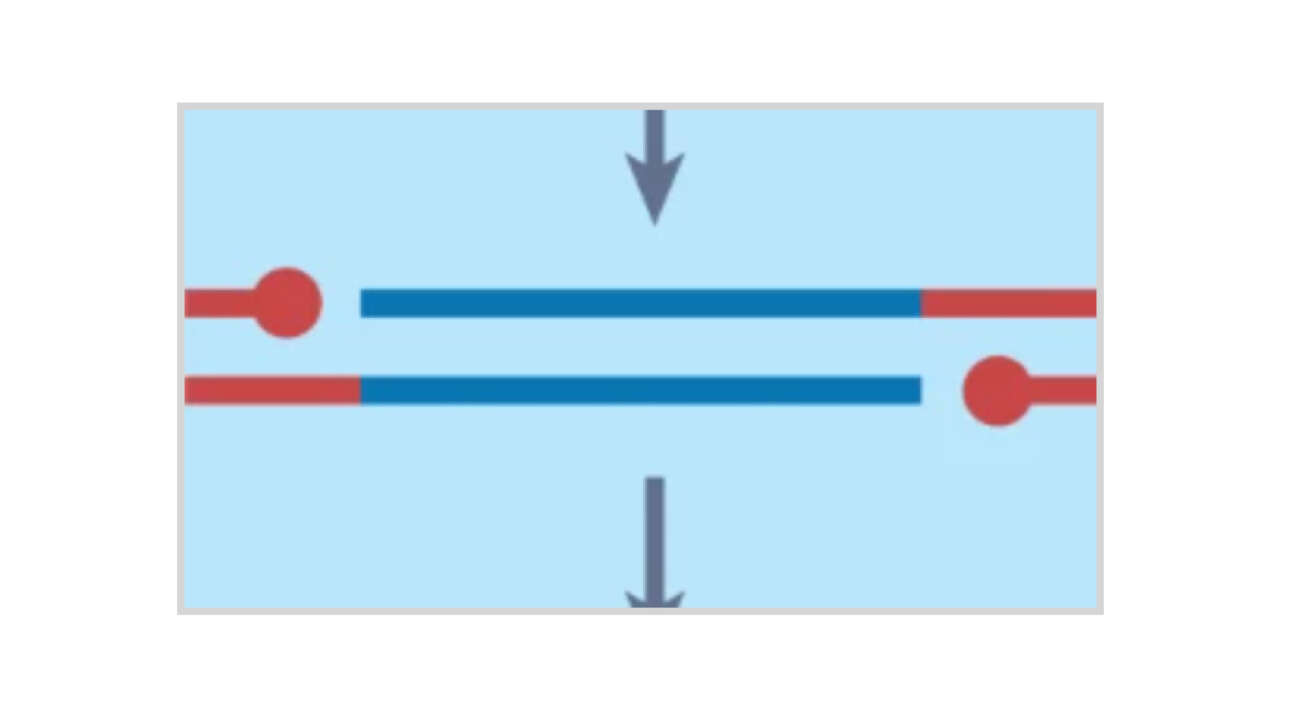
The Ladoux/Mege Lab published a new article in The European Physical Journal E:
Tissue stress measurements with Bayesian inversion stress microscopy
Abstract:
Cells within biological tissue are constantly subjected to dynamic mechanical forces. Measuring the internal stress of tissues has proven crucial for our understanding of the role of mechanical forces in fundamental biological processes like…

The Institut Jacques Monod (CNRS | Paris Cité University) is proud to announce that Stéphane Peyrégne, team leader at the institute, is the winner of the 2025 Georges Brahms Prize awarded by the CNRS Foundation!
© Crédit photo : Marie Origas – CNRS Biologie
Portrait of Stéphane Peyrégne by CNRS Biology and the CNRS Foundation…
The Duharcourt Lab published a new article in Nature reviews molecular cell biology:
Programmed ‘DNA splicing’ removes transposons from genes
Duharcourt S. Programmed 'DNA splicing' removes transposons from genes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2026 Jan 5. doi: 10.1038/s41580-025-00943-z. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 41491422.

The Konstantinides Lab contribued to the writing of the editorial for the January 2026 issue of the European Journal of Neuroscience:
The Power of Diversity in Neuroscience Research Models
Abstract:
Neuroscience thrives on diversity-not only in the questions it asks but also in the models it uses to explore them. Across the field, different animal models have…
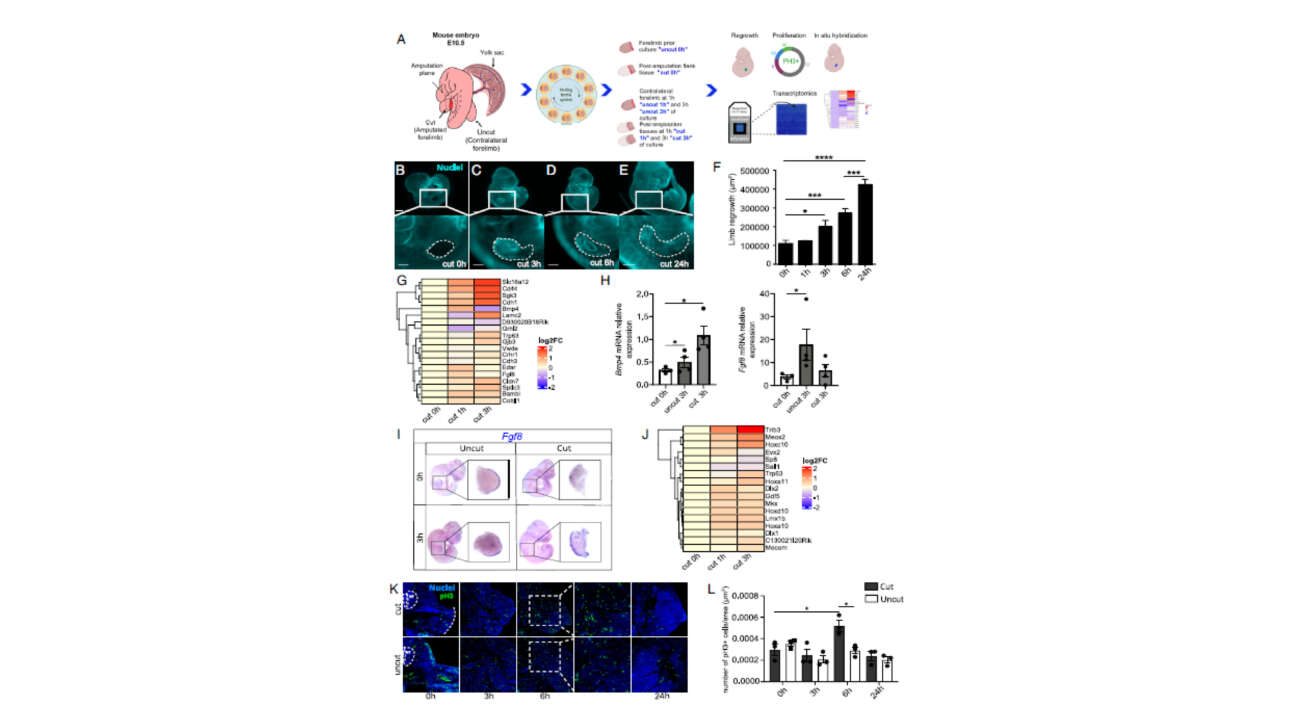
The Collignon Lab contributed to the publication of a new article in PNAS:
Neural crest cell recruitment and reprogramming as central drivers of embryonic limb regeneration
Abstract:
Significance
Mouse embryos possess the remarkable ability to regenerate amputated forelimb buds at E10.5—a capacity lost just 2 d later. We identify neural crest cells (NCCs) as key drivers in…
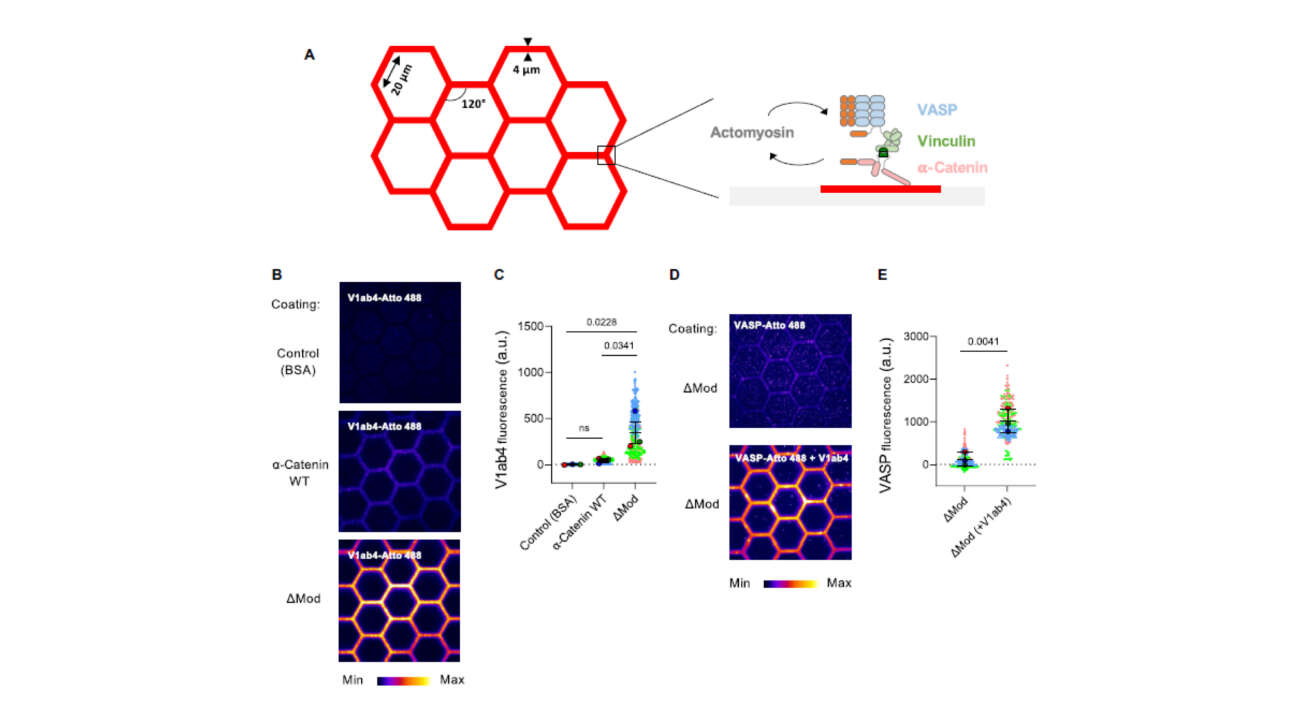
The Ladoux-Mège Lab contributed to the publication of a new article in Science advances:
Actomyosin-dependent assembly of the mechanosensitive machinery from adherens junctions triggers actin polymerization and organization
Abstract:
Cells rely on cadherin-based adherens junctions (AJs) to form cohesive tissues. To establish contact, cells generate pushing forces through branched actin polymerization mediated by the actin-related protein 2/3…

As part of the launch of the Bioengineering flagship initiative of the IdEx FORMULA, bringing together several partner institutes of Université Paris Cité (Cochin Institute, Institut Pasteur, Institut Jacques Monod, MSC, EDC), we are seeking to recruit a Research Engineer (RE).
The successful candidate will be embedded at the Cochin Institute, within the “Leukemia and Niche…

