Regulation of Actin Assembly Dynamics
GUILLAUME ROMET-LEMONNE & ANTOINE JEGOU
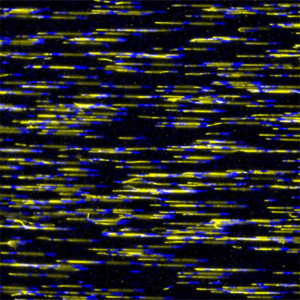
In cells, the assembly of actin filaments is highly regulated to give rise to different actin networks with well-controlled architectures (cortex, lamellipodia, filopodia, …). These networks allow specific cell deformations and movements, required for many processes (motility, division, endocytosis, …).
A large number of proteins interact with actin to control how, where and when actin monomers assemble into filaments. Understanding their biochemical activities can be very difficult to decipher, especially when these activities depend on the local cellular context and the mechanical constraints that apply to each filament forming these networks. Our goal is to understand the elementary processes of actin mechanosensitivity affecting actin dynamics and the action of regulatory proteins. To this end, our team is developing experimental approaches combining microfluidics, micropatterning, and optical tweezers to conduct in vitro experiments that are essential to decipher the individual molecular reactions that regulate the emergence of actin networks.
Keywords: cytoskeleton, actin, biochemistry, biophysics, mechanosensitivity, networks, mechanics
+33 (0)157278013 romet (at) ijm.fr / antoine.jegou (at) ijm.fr @Romet_Jegou_lab www.actindynamics.net
The assembly of ATP-actin monomers into filaments is the basis for the formation of the actin cytoskeleton in cells. The hydrolysis of ATP that occurs during this process is accompanied by a major change in the conformation of the actin subunits, and thus of the filament itself. These changes have profound consequences on the regulation of filament assembly kinetics.
In cells, actin assembly is regulated by hundreds of actin binding proteins (ABPs), which can act together, in synergy, or in competition. These ABPs can bind to the sides, ends of filaments and/or monomers and have various effects. They are generally distinguished according to their main functions: nucleators, elongators, proteins that promote filament disassembly, stabilize filaments, or proteins that link filaments to each other or to other organelles.
If ABPs can modify the mechanical state of actin filaments, external mechanical factors can in turn affect the activity of ABPs. We believe that this mechanochemical interaction plays a crucial role in the assembly of the actin network in cells.
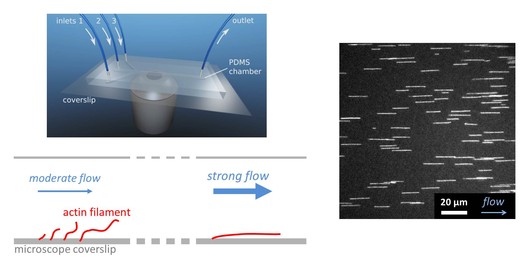
To understand how ABPs and the mechanical context generate networks of various geometries, dynamics and lifetimes, our team focuses its efforts on the observation and in vitro manipulations of single actin filaments or small reconstituted networks under well-controlled conditions. Microfluidics is a very powerful tool to expose filaments to different protein solutions in a sequential manner and to expose filaments to various mechanical stresses, thus opening new avenues to decipher the dynamics of actin network assembly.
On the right, a sketch represents a standard microfluidic chamber with 3 inlets positioned above a microscope objective. In this chamber, actin filaments are grown from primers anchored to the surface of the experimental chamber and aligned with the flow. Dozens of fluorescently labeled actin filaments can be followed in parallel while being exposed to various biochemical conditions affecting their dynamics.
Group Leaders:
Guillaume ROMET-LEMONNE
Téléphone : +33 (0)157278013
Email : romet (at) ijm.fr
Antoine JEGOU
Téléphone : +33 (0)157278013
Email : antoine.jegou (at) ijm.fr
Members:
| Foad | GHASEMI | Doctorant |
| Berengere | GUICHARD | Ingénieure en biologie |
| Camille | BAGES | Ingénieure en biologie |
| Cécile | LEDUC | Chercheur |
| Dina | AL ABYAD | Postdoctorant |
| Inaara | KASSAMALY | Doctorant |
| Ingrid | BILLAULT-CHAUMARTIN | Postdoctorant |
| Jiu | XIAO | Doctorant |
| Lilian | PATY | Master 2 |
| Omar | EL HAMOUI | Postdoctorant |
| Pierre | BONNESOEUR | Ingénieur en biologie |
| Rebecca | PAGES | Assistante ingénieur |
| Wouter | KOOLS | Doctorant |
| Hugo | WIOLAND | Chercheur |
| Zhengdunhuang | XU |
Wioland, H., Jégou, A., and Romet-Lemonne, G. (2022). Celebrating 20 years of live single-actin-filament studies with five golden rules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 119, e2109506119.
Wioland, H., Frémont, S., Guichard, B., Echard, A., Jégou, A., and Romet-Lemonne, G. (2021). Actin filament oxidation by MICAL1 suppresses protections from cofilin-induced disassembly. EMBO Rep. 22, e50965.
Cao, L., Yonis, A., Vaghela, M., Barriga, E.H., Chugh, P., Smith, M.B., Maufront, J., Lavoie, G., Méant, A., Ferber, E., et al. (2020). SPIN90 associates with mDia1 and the Arp2/3 complex to regulate cortical actin organization. Nat. Cell Biol. 1–12.
Hakala, M., Wioland, H., Tolonen, M., Kotila, T., Jegou, A., Romet-Lemonne, G., and Lappalainen, P. (2021). Twinfilin uncaps filament barbed ends to promote turnover of lamellipodial actin networks. Nat. Cell Biol. 23, 147–159.
Jégou, A., and Romet-Lemonne, G. (2020). Mechanically tuning actin filaments to modulate the action of actin-binding proteins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 68, 72–80.
Suzuki, E.L., Chikireddy, J., Dmitrieff, S., Guichard, B., Romet-Lemonne, G., and Jégou, A. (2020). Geometrical Constraints Greatly Hinder Formin mDia1 Activity. Nano Lett. 20, 22–32.
Wioland, H., Jegou, A., and Romet-Lemonne, G. (2019). Torsional stress generated by ADF/cofilin on cross-linked actin filaments boosts their severing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 116, 2595–2602.
Cao, L., Kerleau, M., Suzuki, E.L., Wioland, H., Jouet, S., Guichard, B., Lenz, M., Romet-Lemonne, G., and Jegou, A. (2018). Modulation of formin processivity by profilin and mechanical tension. Elife 7, e34176.
Wioland, H., Guichard, B., Senju, Y., Myram, S., Lappalainen, P., Jégou, A., and Romet-Lemonne, G. (2017). ADF/Cofilin Accelerates Actin Dynamics by Severing Filaments and Promoting Their Depolymerization at Both Ends. Curr. Biol. 27, 1956–1967.e7.
Shekhar, S., Kerleau, M., Kühn, S., Pernier, J., Romet-Lemonne, G., Jégou, A., and Carlier, M.-F. (2015). Formin and capping protein together embrace the actin filament in a ménage à trois. Nat. Commun. 6, 8730.
Jégou, A., Carlier, M.-F., and Romet-Lemonne, G. (2013). Formin mDia1 senses and generates mechanical forces on actin filaments. Nat. Commun. 4, 1883.
Publications
Preprints
Reviews
Foad GHASEMI : 2020-2023.
Léana LENGAGNE : 2021-2024
Jiu XIAO : 2021-2024
-
Institut Jacques Monod
-
The Nicolas Minc Lab
-
The Ladoux-Mège lab
-
-
In France
-
Arnaud Echard (Institut Pasteur, Paris, France)
-
Anne Houdusse (Institut Curie, Paris, France)
-
Aurélie Bertin (Institut Curie, Paris, France)
-
Terence Strick (IBENS, Paris, France)
-
Alexis Gautreau (Ecole Polytechnique, Palaiseau, France)
-
Olivia du Roure and Julien Heuvingh (ESPCI, Paris, France)
-
Martin Lenz (LPTMS, Orsay, France)
-
Christophe Le Clainche (I2BC, Gif/Yvette, France)
-
-
In other countries
-
Ewa Paluch (Univ. of Cambridge, UK)
-
Guillaume Charras (UCL, London, UK)
-
Philippe Roux ( Univ. of Montreal, Canada)
-
Pekka Lappalainen (Univ. of Helsinki, Finland)
-
Daryl Bosco (Univ. Massachusetts Medical School, USA)
-
Till Boecking (Univ. New South Wales, Sydney, Australia)
-
ANR, FRM, INSERM/ITMO, Labex WhoAmI?
4 postdoc positions opened


