Human neurodevelopment and disorders

ERL 1340
Vanessa RIBES / Stéphane NEDELEC
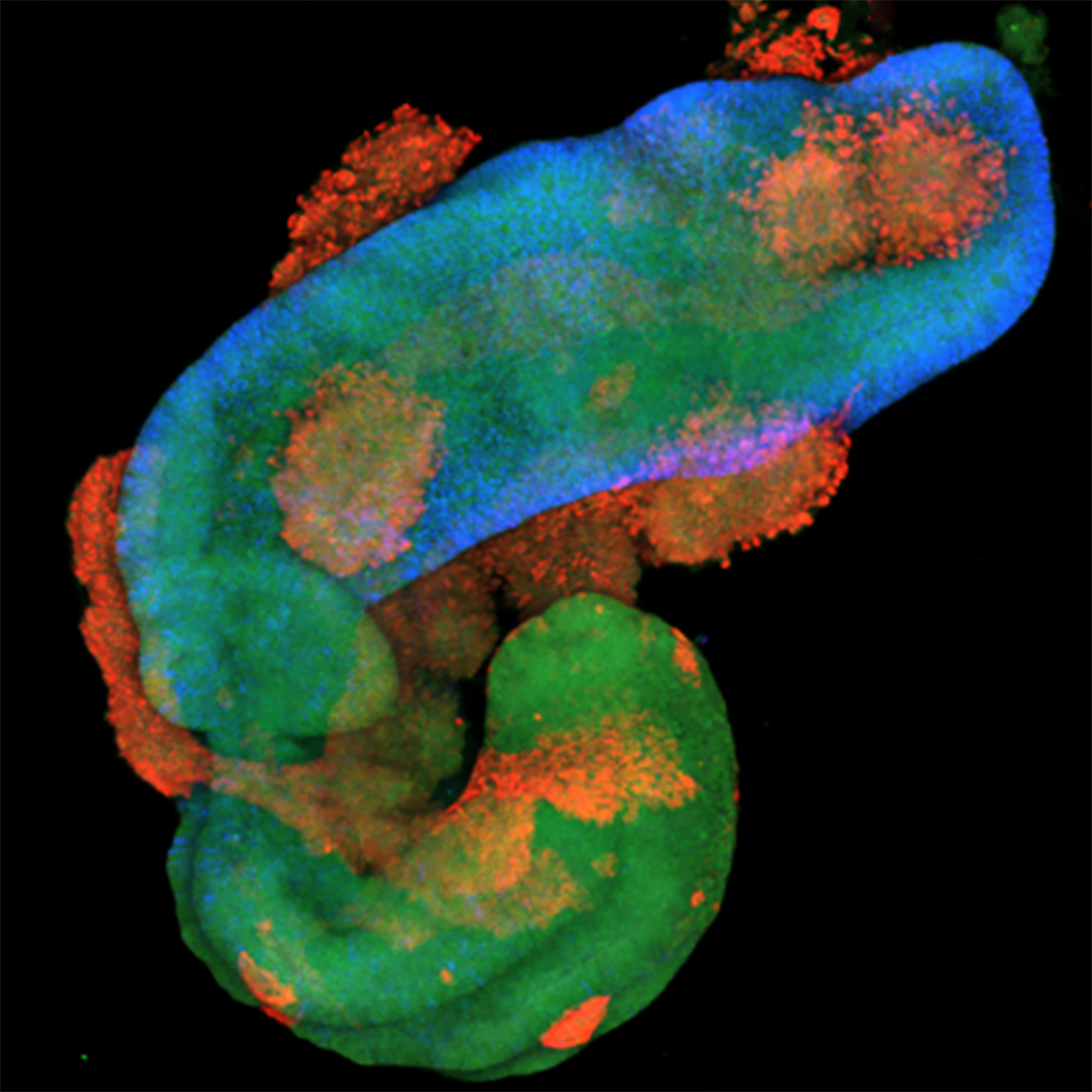
Our team investigates the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying human development and disease, including rhabdomyosarcoma, neural tube defects, spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). To address these questions, we develop and employ organoid models derived from human and mouse pluripotent stem cells.
Keywords: embryo, spinal cord, organoids, human and murine pluripotent stem cells, iPSC, development, signaling pathways, transcription factors, cell fates
+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93 Contact Vanessa Ribes Contact Stéphane Nedelec
Our research primarily focus on the development of the spinal cord and hindbrain.
Our goals are to:
- Elucidate the dynamics of signaling pathways and transcriptional programs that orchestrate neural tube morphogenesis and drive the emergence of the diverse progenitor and neuronal populations that form sensory and motor circuits.
- Decipher how rare genetic mutations disrupt these developmental processes, leading to neural tube defects, pediatric cancers—particularly rhabdomyosarcoma—and motor neuron diseases such as spinal muscular atrophy and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Axis 1: PAX3/7 and BMPs – Spatial Regulation of Cell Fates and Morphologies
The paralogous transcription factors PAX3 and PAX7 can function both as transcriptional activators and repressors. This functional duality is modulated along the dorsoventral axis of the embryonic spinal cord by the BMP signaling gradient, with each function determining specific cell fates and morphologies. We aim to decipher how this dual activity is integrated at the genomic level by analyzing the recruitment of PAX proteins and their partners, as well as the associated chromatin dynamics. In parallel, we are investigating how the gene networks regulated by PAX orchestrate their effects on cell fate, morphology, and the mechanical properties of the neuroepithelium. This research seeks to provide insights into how mutations affecting PAX or their regulatory networks lead to defects in neural tube closure and neurogenesis, underlying a major congenital condition: spina bifida.
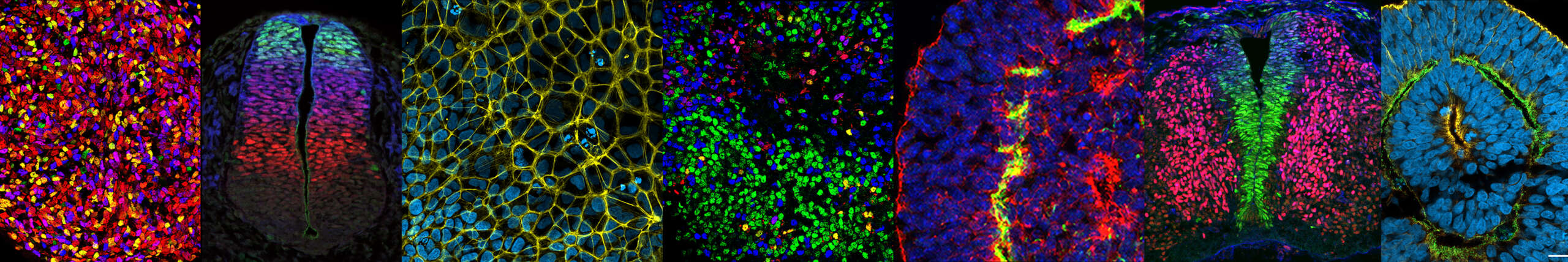
Axis 2: Signaling Dynamics and specification of hindbrain and spinal neuronal diversity
Using targeted differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) and organoid models we have developed over the years, we investigate the signal transduction pathways and genetic networks that control the coupling of neural tube morphogenesis and patterning. This ensures the formation of distinct locomotor neural circuits along the body axis (Nedelec, Martinez-Arias, Curr. Opin. Neurobiol., 2021).
We developed a new strategy to study cell fate mechanisms via in vitro differentiation of hPSCs (Maury et al., Nature Biotechnology, 2015), enabling efficient specification of hindbrain and axial spinal progenitors and their differentiation into spinal and cranial motor neurons—cell types that show differential vulnerability in disease. These models allowed us to uncover mechanisms regulating the sequential expression of HOX genes, which are master regulators of motor circuit diversification along the antero-posterior axis.
This work led to the first efficient methods for generating distinct motor neuron subtypes differentially impacted in motor neuron diseases (Mouilleau, Vaslin et al., Development, 2021).
By investigating how axial progenitor fate and morphogenetic potential are regulated, we recently identified key signaling pathways that coordinate co-morphogenesis and patterning of the neural tube and somites. This enabled the in vitro generation of human trunk-like structures modeling the morphogenesis of the developing body axis and led to the identification of pathways controlling neural tube morphogenesis.
These studies show that stem cell self-organizing models can recapitulate multi-tissue morphogenesis and the topographic organization of terminal cell types—features absent in most current organoid systems. This opens new avenues for modeling human organogenesis and studying the development and function of neural tube and sensory-motor circuits (Gribaudo et al., Nature Biotechnology, 2024).
Ongoing Projects in this axis
1. Synchronization of antero-posterior axis morphogenesis and Patterning
How is morphogenesis of the antero-posterior axis synchronized with its patterning to ensure proper allocation of cell types?
We use perturbations of signaling dynamics and genomic analyses (RNA-seq, ATAC-seq, CUT&Tag) to study how extrinsic cues driving embryonic axis elongation regulate HOX gene induction. We aim to understand how the tempo of HOX activation translates into spatial patterns of expression that position distinct neuronal subtypes along the axis.
2. Specification of Human Motor Neuron Diversity
The human body contains over 300 distinct skeletal muscles, each innervated by a motor pool—a dedicated group of motor neurons. Yet, our understanding of the mechanisms ensuring this neuronal diversification, especially in humans, remains limited with important consequences on the validity of in vitro models.
Using a combination of bulk and single-cell genomic analyses in both organoid and embryonic tissues, we study the intrinsic and extrinsic cues that drive spinal neuronal diversity, focusing initially on the specification of motor neuron subtypes.
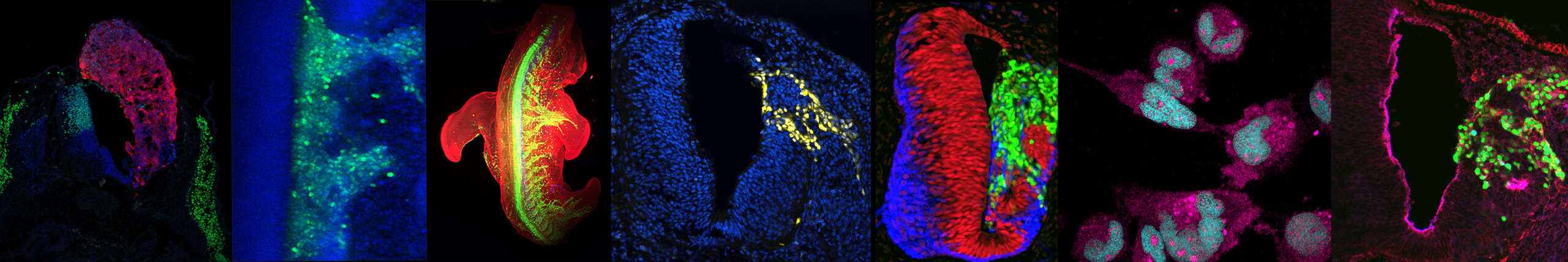
Axis 3: Cellular and Molecular Basis of Motor Neuron Disease
These in vitro models provide access to human tissues or cell types affected in various diseases. We use patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells and in vitro embryogenesis models to study the foundations of motor neuron diseases—an heterogeneous group of incurable and often fatal disorders. Our focus is on infantile spinal muscular atrophies (SMAs), which, although caused by mutations in ubiquitously expressed genes, are associated with defects in the formation or survival of specific motor neuron populations, while others remain unaffected. Deciphering the basis of vulnerability or resilience in these distinct motor neuron subtypes could pave the way for novel therapeutic strategies. Building on these approaches, we are initiating a project on amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in collaboration with Odil Porrua.
Axis 4: Hijacking Neurodevelopmental Signals in Rhabdomyosarcoma
The ectopic activation of developmental signaling pathways in pediatric cancers, including rhabdomyosarcoma, may explain their rapid progression without the accumulation of typical proto-oncogenic aberrations. In this project, we assess the potential of neuronal cells to give rise to neoplasms resembling rhabdomyosarcoma. In collaboration with M. Castets (CRCL) and E. Pasquier (CRCM), we investigate the role of neurodevelopmental signals in the emergence of this cancer and explore the possibility of targeting these signals to sensitize rhabdomyosarcoma cells to existing chemotherapy treatments.
Team leaders
 Stephane NEDELEC, Researcher, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 91, room 555B
Stephane NEDELEC, Researcher, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 91, room 555B Vanessa RIBES, Researcher, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 555B
Vanessa RIBES, Researcher, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 555B
Members
 Asna ABDOU, Biology engineer, RIBES/NEDELEC LABroom 583B
Asna ABDOU, Biology engineer, RIBES/NEDELEC LABroom 583B Ada ALLAM, Postdoctoral researcher, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB
Ada ALLAM, Postdoctoral researcher, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB Marine ALVES, Biology engineer, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 583B
Marine ALVES, Biology engineer, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 583B Kenza CHERIET, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 555B
Kenza CHERIET, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 555B Lucas DENIS, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93
Lucas DENIS, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93 Claire DUGAST, Assistant Professor, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 555B
Claire DUGAST, Assistant Professor, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 555B Pascale GILARDI HEBENSTREIT, Researcher, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 583B
Pascale GILARDI HEBENSTREIT, Researcher, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 583B Marine GRISON, Biology engineer, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 590B
Marine GRISON, Biology engineer, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 590B Grace HENSTONE, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 555B
Grace HENSTONE, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 555B Theaud HEZEZ, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 590B
Theaud HEZEZ, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 590B Helena MALEK, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 555B
Helena MALEK, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 555B Camil MIRDASS, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 590B
Camil MIRDASS, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 590B Carla RODRIGUEZ-VILLA, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB
Carla RODRIGUEZ-VILLA, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB Robin RONDON, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 590B
Robin RONDON, PhD student, RIBES/NEDELEC LAB+33 (0)1 57 27 81 93, room 590B
To contact a member of the team by e-mail: name.surname@ijm.fr

Stem cell-derived models of spinal neurulation. Mirdass C, Catala M, Bocel M, Nedelec S, Ribes V. Emerg Top Life Sci. 2023 Dec 18;7(4):423-437. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20230087. PMID: 38087891 Review.
Self-organizing models of human trunk organogenesis recapitulate spinal cord and spine co-morphogenesis. Gribaudo S, Robert R, van Sambeek B, Mirdass C, Lyubimova A, Bouhali K, Ferent J, Morin X, van Oudenaarden A, Nedelec S. Nat Biotechnol. 2024 Aug;42(8):1243-1253. doi: 10.1038/s41587-023-01956-9. Epub 2023 Sep 14. PMID: 37709912
Single-cell transcriptomic analysis reveals diversity within mammalian spinal motor neurons. Liau ES, Jin S, Chen YC, Liu WS, Calon M, Nedelec S, Nie Q, Chen JA. Nat Commun. 2023 Jan 3;14(1):46. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35574-x. PMID: 36596814 Free PMC article.
Dynamic extrinsic pacing of the HOX clock in human axial progenitors controls motor neuron subtype specification. Mouilleau V, Vaslin C, Robert R, Gribaudo S, Nicolas N, Jarrige M, Terray A, Lesueur L, Mathis MW, Croft G, Daynac M, Rouiller-Fabre V, Wichterle H, Ribes V, Martinat C, Nedelec S. Development. 2021 Mar 29;148(6):dev194514. doi: 10.1242/dev.194514.
The PAX-FOXO1s trigger fast trans-differentiation of chick embryonic neural cells into alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma with tissue invasive properties limited by S phase entry inhibition. Gonzalez Curto G, Der Vartanian A, Frarma YE, Manceau L, Baldi L, Prisco S, Elarouci N, Causeret F, Korenkov D, Rigolet M, Aurade F, De Reynies A, Contremoulins V, Relaix F, Faklaris O, Briscoe J, Gilardi-Hebenstreit P, Ribes V. PLoS Genet. 2020 Nov 11;16(11):e1009164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009164.
In vitro models of spinal motor circuit’s development in mammals: achievements and challenges. Nedelec S, Martinez-Arias A. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2021 Feb;66:240-249. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2020.12.002. Epub 2021 Mar 5. PMID: 33677159 Review.
Dullard-mediated Smad1/5/8 inhibition controls mouse cardiac neural crest cells condensation and outflow tract septation. Darrigrand JF, Valente M, Comai G, Martinez P, Petit M, Nishinakamura R, Osorio DS, Renault G, Marchiol C, Ribes V, Cadot B. Elife. 2020 Feb 27;9:e50325. doi: 10.7554/eLife.50325.
BMP4 patterns Smad activity and generates stereotyped cell fate organization in spinal organoids. Duval N, Vaslin C, Barata TC, Frarma Y, Contremoulins V, Baudin X, Nedelec S, Ribes VC. Development. 2019 Jul 25;146(14):dev175430. doi: 10.1242/dev.175430.
Pax3- and Pax7-mediated Dbx1 regulation orchestrates the patterning of intermediate spinal interneurons. Gard C, Gonzalez Curto G, Frarma YE, Chollet E, Duval N, Auzié V, Auradé F, Vigier L, Relaix F, Pierani A, Causeret F, Ribes V. Dev Biol. 2017 Dec 1;432(1):24-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.06.014.
Combinatorial analysis of developmental cues efficiently converts human pluripotent stem cells into multiple neuronal subtypes. Maury Y, Côme J, Piskorowski RA, Salah-Mohellibi N, Chevaleyre V, Peschanski M, Martinat C, Nedelec S. Nat Biotechnol. 2015 Jan;33(1):89-96. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3049. Epub 2014 Nov 10. PMID: 25383599
Publications
- Maeliss Calon: “Study of the Molecular and Cellular Bases of Motor Neuron Vulnerability in Distal Spinal Muscular Atrophy of the Lower Limbs”, defended on September 26, 2024.
- Rémi Robert: “Study of the Mechanisms Controlling HOX Gene Expression and Implications for the In Vitro Generation of Human Tissues”, defended on September 22, 2023.
- Line Manceau: “Study of the Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Through Which the Paralogous Transcription Factors PAX3-FOXO1 and PAX7-FOXO1 Exert Their Oncogenic Activity”, defended on September 24, 2021.
- Célia Vaslin: “Study of the Cellular Signaling Mechanisms Controlling Neuronal Diversification in the Spinal Cord”, defended on March 26, 2021.
- Vincent Mouilleau: “Study of the Mechanisms of Human Spinal Cord Development Through the Establishment of In Vitro Models Derived from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells”, defended on November 26, 2019.
- Nicolas Borghi (IJM)
- Valérie Doye (IJM)
- Alexandre Baffet (Institut Curie, France)
- Nadia Bahi-Buisson (Institut Imagine, France)
- Bertrand Bénazéraf (Centre de Biologie Intégrative, CBI, France)
- Jésus Lacal (University of Salamanca, Spain)
- Marie Castets (Centre de Recherche en Cancérologie de Lyon, CRCL, Lyon)
- Valérie Dupé (Institut Génétique & Développement de Rennes, IGDR, Rennes)
- Fiona Francis (Institut du Fer à Moulin, IFM, France)
- Eddy Pasquier (Centre de Recherche en Cancérologie de Marseille, CRCM, Marseille)
- Alessandra Pierani (Institut Imagine, France)
- Benoit Sorre (Institut Curie, France)
- Hynek Wichterle (Columbia University, New York, USA)
- Odil Porrua (IGMM, Montpellier, France)
- INSERM
- Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer
- Agence Nationale de la Recherche
- Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale
- L’association WonderAugustine
- Financement “Emergence en recherche” (Université Paris Cité)
- PEPR Cell-ID
- ibio Sorbonne université
- GIS FC3R
Post-doctoral positions
We are looking for postdoctoral candidates interested in working on transcriptional regulation of cell fate decisions, with expertise in iPSC culture or bioinformatics. Applicants should email to stephane.nedelec@ijm.fr with their CV, motivation letter and contact details for 2-3 referees.
Master students
We are currently looking for a Master 2 student, with interest in regulation of chromatin states during neural development (stephane.nedelec@ijm.fr) or cancer emergence (vanessa.ribes@ijm.fr). Students with a background in mathematics or computational science are encouraged to apply. Applicants should send us a CV and motivation letter.

