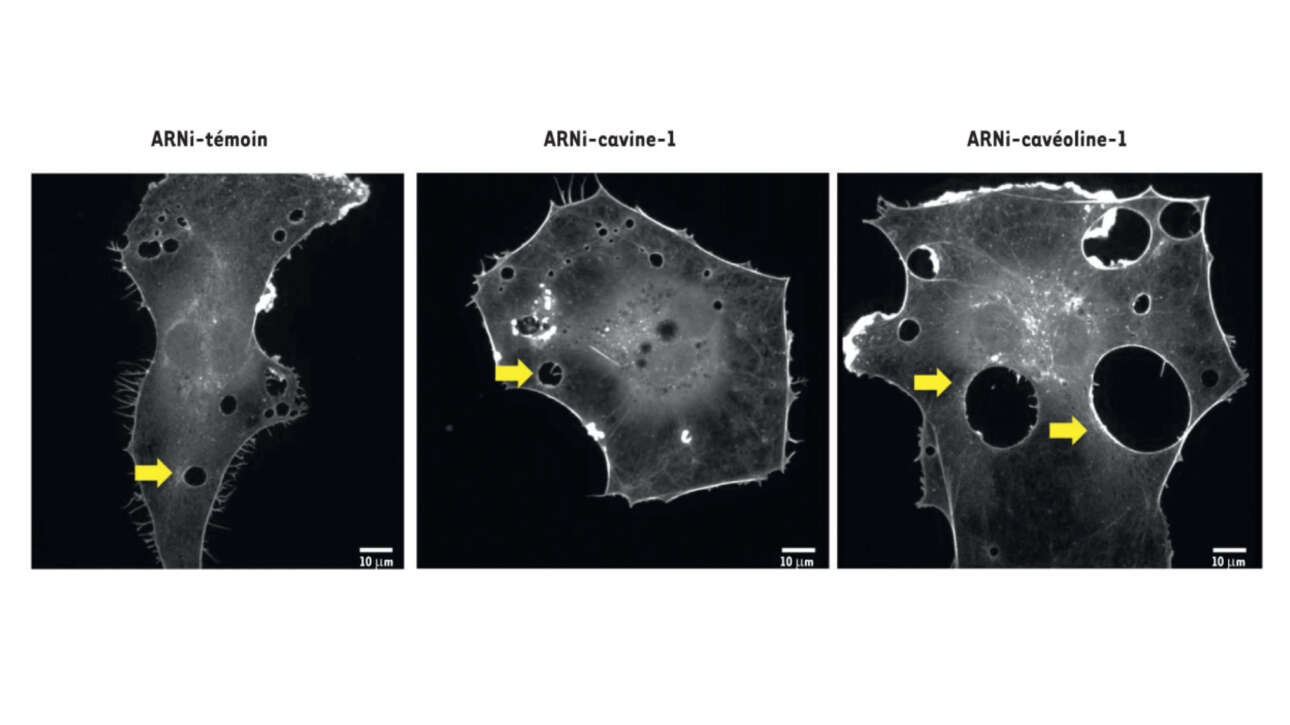
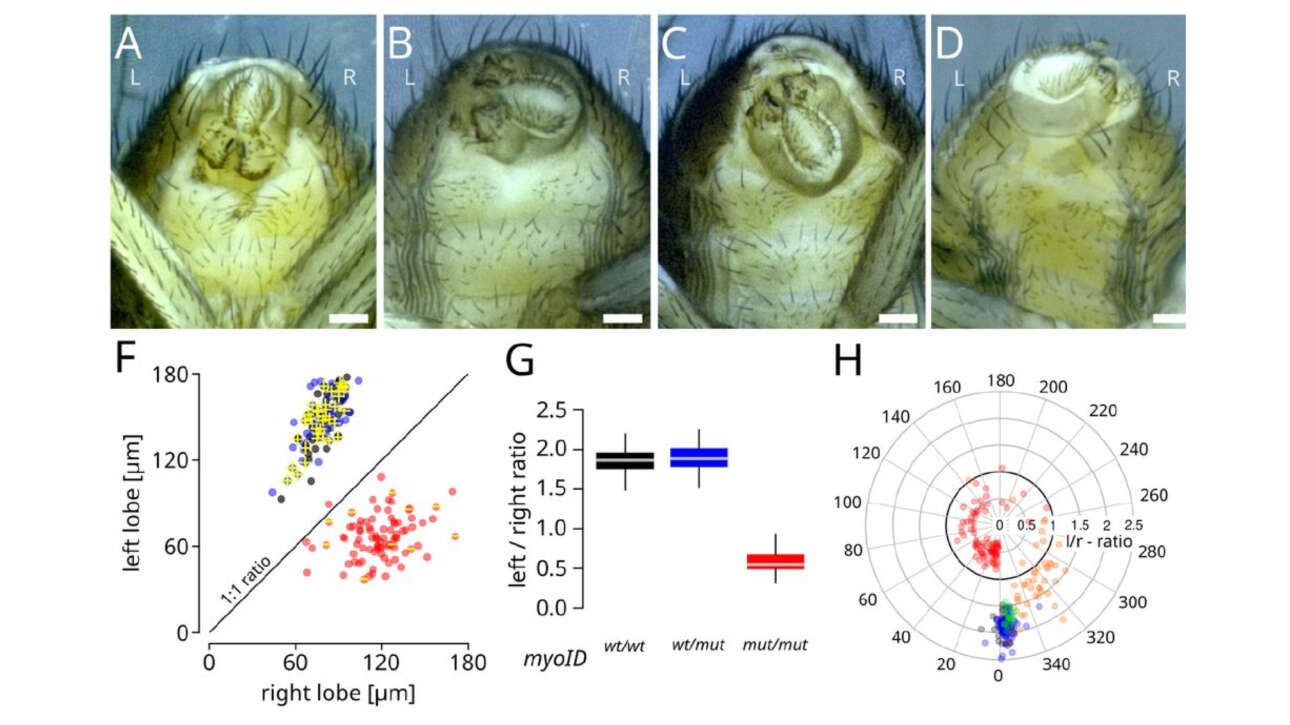
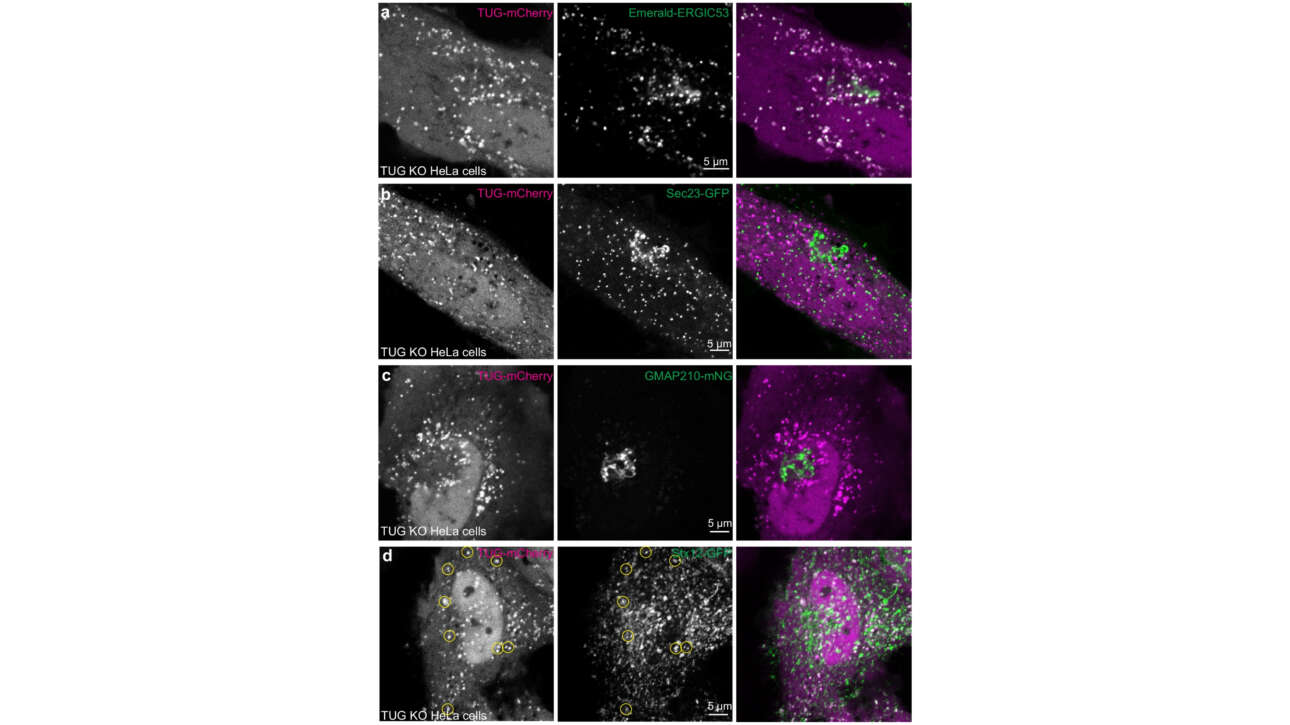
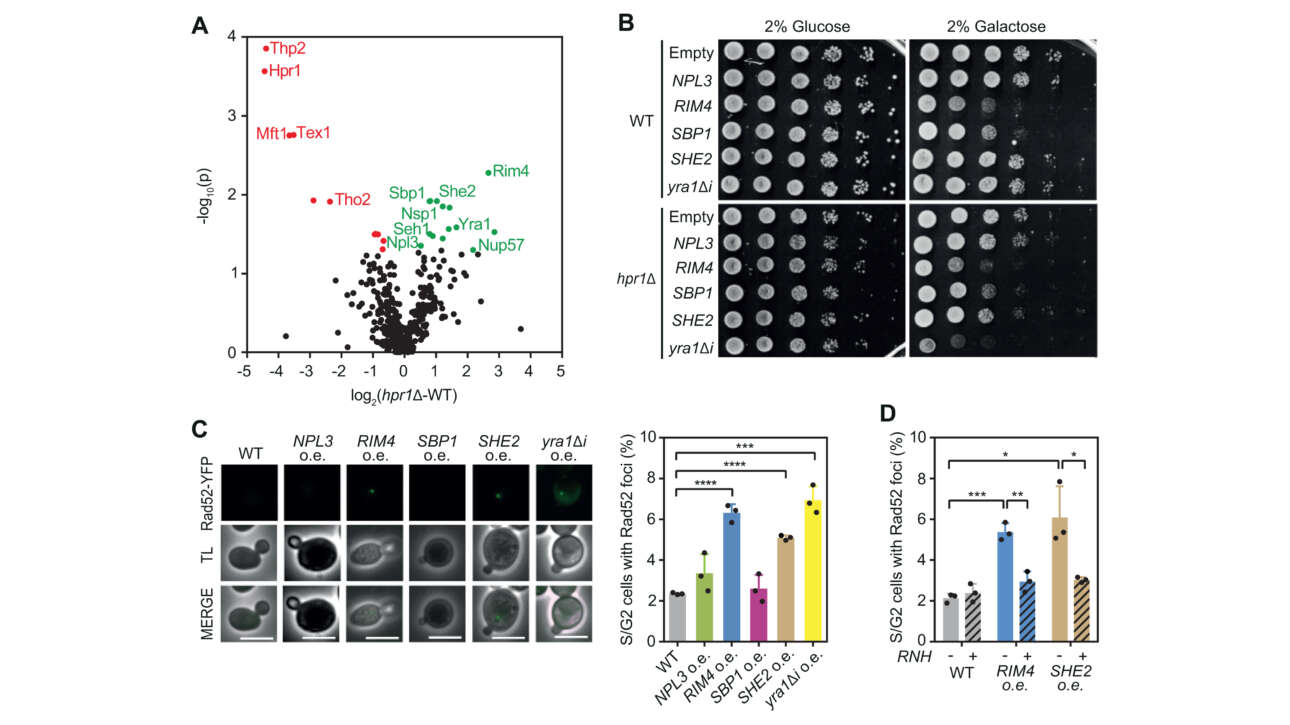
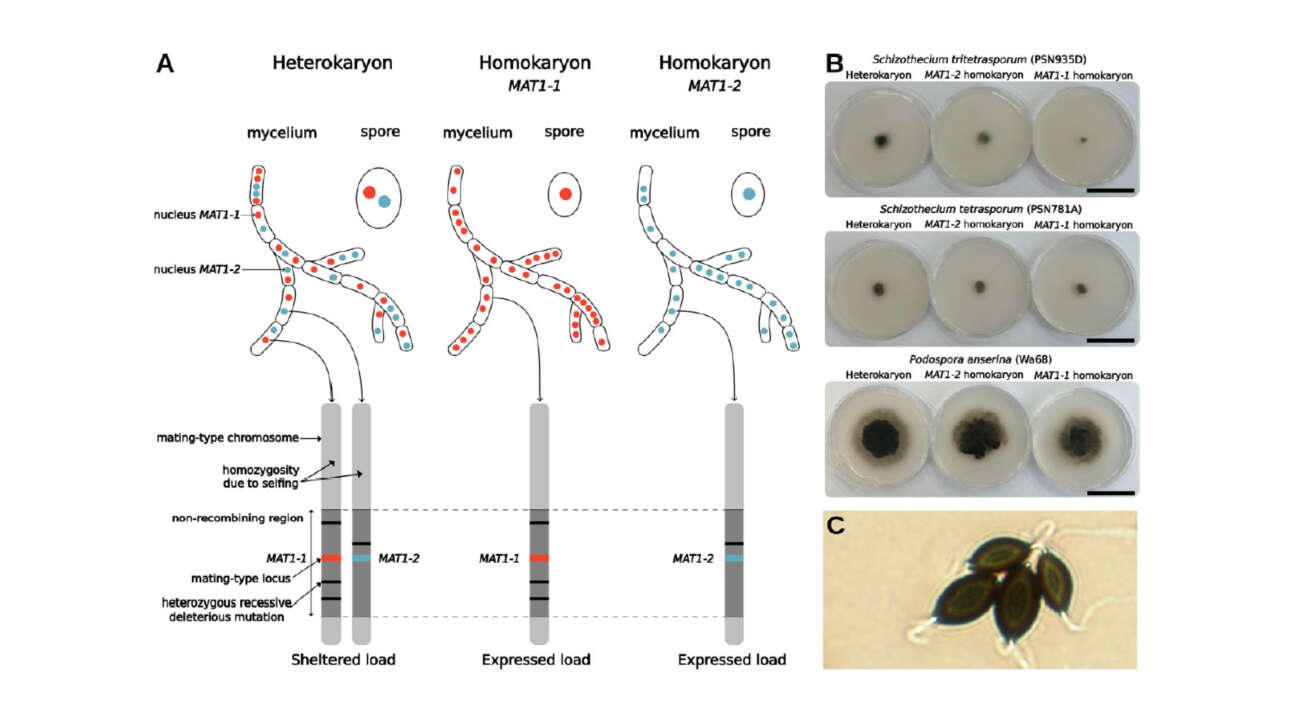
L'équipe Romet-Lemonne/Jégou a contribué à la publication d'un nouvel article dans médecine/science :
La cavéoline-1 rigidifie la membrane plasmique et limite l’expansion de tunnels transcellulaires
Lemichez E, Morel C, Leduc C, Bassereau P. La cavéoline-1 rigidifie la membrane plasmique et limite l’expansion de tunnels transcellulaires [Caveolin-1 stiffens the plasma membrane and limits transcellular tunnel expansion]. Med…