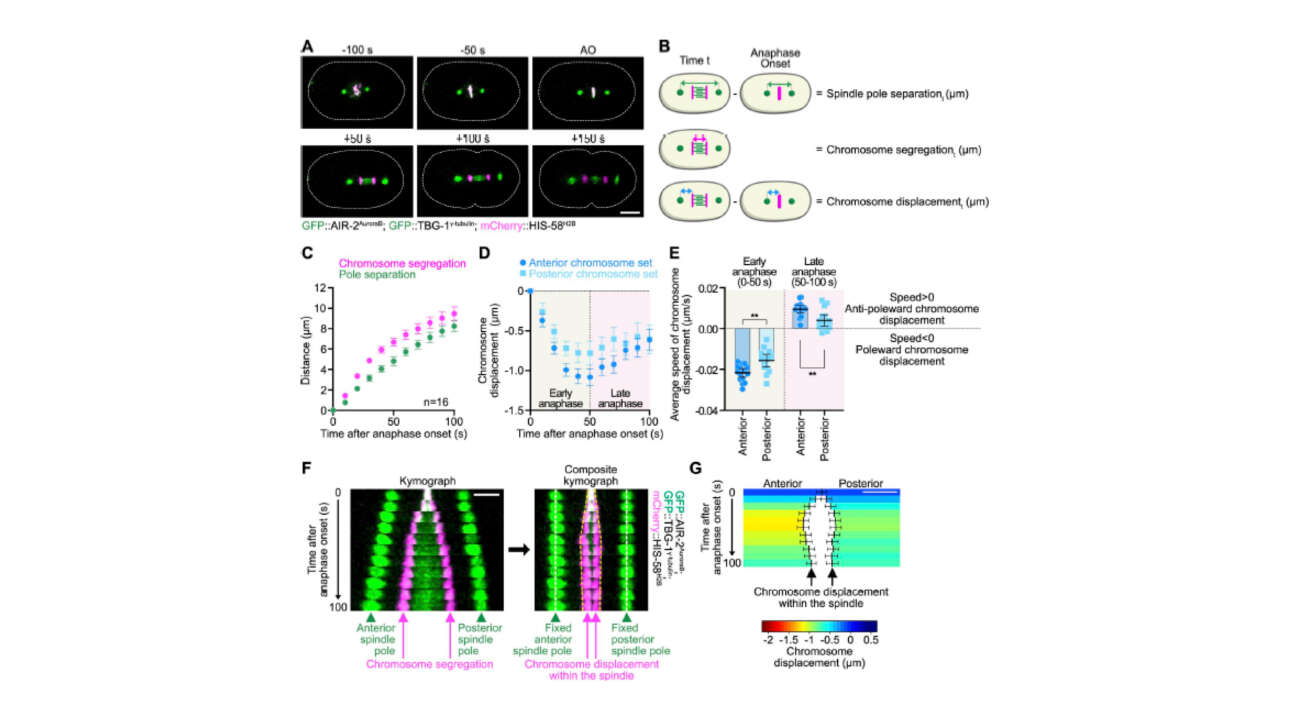
L'équipe Dumont a publié un nouvel article dans Journal of Cell Biology :
Mechanical coordination between anaphase A and B drives asymmetric chromosome segregation
L'équipe Minc de l'Institut Jacques Monod a également contribué à cet article.
Résumé :
Chromosome segregation during anaphase occurs through two mechanistically distinct processes: anaphase A, in which chromosomes move toward spindle poles, and…